Transferrin receptor 2 and HFE regulate furin expression via mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/Erk) signaling. Implications for transferrin-dependent hepcidin regulation
- PMID: 20634490
- PMCID: PMC2966904
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2010.027003
Transferrin receptor 2 and HFE regulate furin expression via mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/Erk) signaling. Implications for transferrin-dependent hepcidin regulation
Abstract
Background: Impaired regulation of hepcidin in response to iron is the cause of genetic hemochromatosis associated with defects of HFE and transferrin receptor 2. However, the role of these proteins in the regulation of hepcidin expression is unclear.
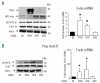
Design and methods: Hepcidin expression, SMAD and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) phosphorylation and furin expression were analyzed in hepatic HepG2 cells in which HFE and transferrin receptor 2 were down-regulated or expressed, or furin activity specifically inhibited. Furin expression was also analyzed in the liver of transferrin receptor 2 null mice.
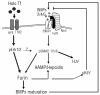
Results: We showed that the silencing of HFE and transferrin receptor 2 reduced both Erk phosphorylation and furin expression, that the exogenous expression of the two enhanced the induction of phosphoErk1/2 and furin by holotransferrin, but that this did not occur when the pathogenic HFE mutant C282Y was expressed. Furin, phosphoErk1/2 and phosphoSMAD1/5/8 were down-regulated also in transferrin receptor 2-null mice. Treatment of HepG2 cells with an inhibitor of furin activity caused a strong suppression of hepcidin mRNA, probably due to the inhibition of bone morphogenic protein maturation.
Conclusions: The data indicate that transferrin receptor 2 and HFE are involved in holotransferrin-dependent signaling for the regulation of furin which involved Erk phosphorylation. Furin in turn may control hepcidin expression.
Figures
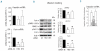




References
-
- Ganz T. Hepcidin–a regulator of intestinal iron absorption and iron recycling by macrophages. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2005;18(2):171–82. - PubMed
-
- Wang RH, Li C, Xu X, Zheng Y, Xiao C, Zerfas P, et al. A role of SMAD4 in iron metabolism through the positive regulation of hepcidin expression. Cell Metab. 2005;2(6):399–409. - PubMed
-
- Zhang AS, West AP, Jr, Wyman AE, Bjorkman PJ, Enns CA. Interaction of hemojuvelin with neogenin results in iron accumulation in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(40):33885–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

