Enzyme replacement therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis VI: Growth and pubertal development in patients treated with recombinant human N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase
- PMID: 20634905
- PMCID: PMC2904323
- DOI: 10.3233/PRM-2010-0113
Enzyme replacement therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis VI: Growth and pubertal development in patients treated with recombinant human N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase
Abstract
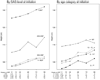
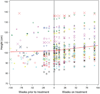
BACKGROUND AND METHODS: Growth failure is characteristic of untreated mucopolysaccharidosis type VI (MPS VI: Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome). Growth was studied in fifty-six MPS VI patients (5 to 29 years old) prior to and for up to 240 weeks of weekly infusions of recombinant human arylsulfatase B (rhASB) at 1 mg/kg during Phase 1/2, Phase 2, Phase 3 or Phase 3 Extension clinical trials. Height, weight, and Tanner stage data were collected. Pooled data were analyzed to determine mean height increase by treatment week, growth impacts of pubertal status, baseline urinary GAG, and age at treatment initiation. Growth rate for approximately 2 years prior to and following treatment initiation was analyzed using longitudinal modeling. RESULTS: Mean height increased by 2.9 cm after 48 weeks and 4.3 cm after 96 weeks on enzyme replacement therapy (ERT). Growth on ERT was not correlated with baseline urinary GAG. Patients under 16 years of age showed greatest increases in height on treatment. Model results based on pooled data showed significant improvement in growth rate during 96 weeks of ERT when compared to the equivalent pretreatment time period. Delayed pubertal onset or progression was noted in 10 patients entering the clinical trials; all of whom showed progression of at least one Tanner stage during 2 years on ERT, and 6 of whom (60%) completed puberty. CONCLUSION: Analysis of mean height by treatment week and longitudinal modeling demonstrate significant increase in height and growth rate in MPS VI patients receiving long-term ERT. This impact was greatest in patients aged below 16 years. Height increase may result from bone growth and/or reduction in joint contractures. Bone growth and resolution of delayed puberty may be related to improvements in general health, bone cell health, nutrition, endocrine gland function and reduced inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Harmatz, Beck, Giugliani, Berger, Steiner and Yu have provided consulting support to BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., Novato, CA. Dr. Hopwood has received commercial research project funding to assist the development of enzyme replacement therapy for MPS VI patients. Drs. Harmatz, Arash and Beck each report receiving speaker’s honorarium and travel support from BioMarin. BioMarin is a supporter of the Lysosomal Disease Network’s WORLD Symposium organized by Dr. Whitley. Drs. Swiedler and Decker are former and current employees of BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., respectively; both are stockholders.
Figures


References
-
- Abbassi V. Growth and normal puberty. Pediatrics. 1998;102(2 Pt 3):507–511. - PubMed
-
- Buyukgebiz B, et al. Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome associated with growth hormone deficiency. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism. 1995;8(4):305–307. - PubMed
-
- Byers S, et al. Effect of enzyme replacement therapy on bone formation in a feline model of mucopolysaccharidosis type VI. Bone. 1997;21(5):425–431. - PubMed
-
- Clarke LA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of laronidase in the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis I. Pediatrics. 2009;123(1):229–240. - PubMed
-
- Concolino D, et al. Precocious puberty in Sanfilippo IIIA disease: diagnosis and follow-up of two new cases. Eur J Med Genet. 2008;51(5):466–471. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

