Safety and efficacy of a new percutaneously implantable interspinous process device
- PMID: 20635103
- PMCID: PMC3128705
- DOI: 10.1007/s00701-010-0740-4
Safety and efficacy of a new percutaneously implantable interspinous process device
Abstract
Background: Lumbar spinal stenosis is a degenerative disease of the elderly population. Although microsurgical decompression has shown good long-term results, percutaneous techniques could provide an alternative in the presence of significant comorbidities.
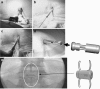
Method: Eighty-seven interspinous process decompression devices (In-space; Synthes, Umkirch, Germany) were implanted percutaneously in up to three segments of 50 patients. Outcome was assessed directly after surgery, at 6-8 weeks, and at average follow-up of 1 year (11.8 ± 6 months). Assessment included complications, pain and spinal claudication, neurodeficit, time to recurrence of symptoms, and time to second surgery. Subgroups with additional low back pain at presentation and mild spondylolisthesis were analyzed separately.
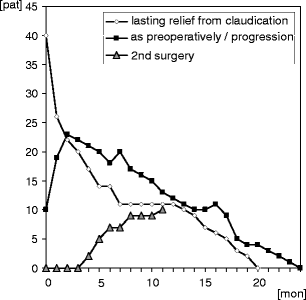
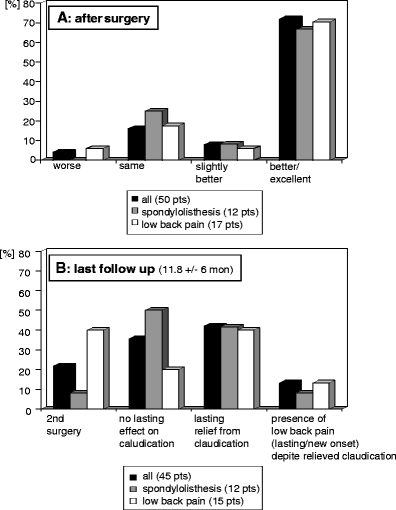
Findings: Intraoperative complications were rare (one misplacement and two cases of failed implantation); average operation time was 16.4 ± 12.2 min per segment. Initial response was very good with 72% good or excellent relief of symptoms. After a 1-year follow-up, 42% reported of lasting relief from spinal claudication. Thirteen percent of these complained about lasting or new-onset low back pain. A second surgery had been performed in 22%. Subgroup analysis was performed for patients presenting with additional low back pain and spondylolisthesis patients. No significant differences could be noted between subgroups.
Conclusions: The In-space is a percutaneous treatment option of claudication in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Compared with microsurgical decompression surgery, recurrence rate within 1 year is, however, high and the device seems not suitable for the treatment of low back pain. Therefore, the authors suggest that the device should presently be used primarily in controlled clinical trials in order to get more information concerning the optimal indication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Felix-trial. Double-blind randomization of interspinous implant or bony decompression for treatment of spinal stenosis related intermittent neurogenic claudication.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010 May 27;11:100. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-11-100. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010. PMID: 20507568 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does an interspinous device (Coflex) improve the outcome of decompressive surgery in lumbar spinal stenosis? One-year follow up of a prospective case control study of 60 patients.Eur Spine J. 2010 Feb;19(2):283-9. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1229-9. Epub 2009 Dec 5. Eur Spine J. 2010. PMID: 19967546 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dynamic interspinous process stabilization: review of complications associated with the X-Stop device.Neurosurg Focus. 2010 Jun;28(6):E8. doi: 10.3171/2010.3.FOCUS1047. Neurosurg Focus. 2010. PMID: 20568923
-
[The importance of interspinous spacers in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis].Orthopade. 2019 Oct;48(10):831-836. doi: 10.1007/s00132-019-03772-z. Orthopade. 2019. PMID: 31297556 Review. German.
-
Interspinous process decompression (IPD) system (X-STOP) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis.Surg Technol Int. 2006;15:265-75. Surg Technol Int. 2006. PMID: 17029185 Review.
Cited by
-
A Differential Clinical Benefit Examination of Full Lumbar Endoscopy vs Interspinous Process Spacers in the Treatment of Spinal Stenosis: An Effect Size Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes.Int J Spine Surg. 2022 Feb;16(1):102-123. doi: 10.14444/8200. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Int J Spine Surg. 2022. PMID: 35177530 Free PMC article.
-
The use of minimally invasive interspinous process devices for the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis: a narrative literature review.J Spine Surg. 2021 Sep;7(3):394-412. doi: 10.21037/jss-21-57. J Spine Surg. 2021. PMID: 34734144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of lumbar interspinous distraction on the neural elements.Neurosurg Rev. 2012 Oct;35(4):477-84; discussion 484. doi: 10.1007/s10143-012-0394-1. Epub 2012 May 2. Neurosurg Rev. 2012. PMID: 22549123 Review.
-
One-year follow-up of a series of 100 patients treated for lumbar spinal canal stenosis by means of HeliFix interspinous process decompression device.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:176936. doi: 10.1155/2014/176936. Epub 2014 Apr 15. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24822181 Free PMC article.
-
[Spinal column: implants and revisions].Chirurg. 2016 Mar;87(3):202-7. doi: 10.1007/s00104-015-0119-4. Chirurg. 2016. PMID: 26779646 German.
References
-
- Barbagallo GM, Olindo G, Corbino L, Albanese V. Analysis of complications in patients treated with the X-Stop Interspinous Process Decompression System: proposal for a novel anatomic scoring system for patient selection and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2009;65(1):111–19. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000346254.07116.31. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

