Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-alpha) isoforms in rodents
- PMID: 20635575
- PMCID: PMC6042024
- DOI: 10.3727/105221610x12717040569901
Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-alpha) isoforms in rodents
Abstract
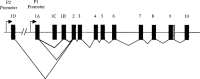
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-alpha) regulates expression of a number of genes in several metabolic organs. The HNF4-alpha gene has two promoters and encodes at least nine isoforms through differential splicing. In mouse liver, transcription initiates at promoter 2 (P2) during fetal life, but switches to P1 at birth. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of HNF4-alpha in other organs is largely unknown. Here, we examined expression of P1- and P2-derived transcripts in a number of mouse and rat tissues. Both P1 and P2 were active in mouse fetal liver, but P2-derived isoforms were detected 50% more abundantly than P1 transcripts. Conversely, the adult mouse liver expressed significantly higher levels of P1- than P2-derived mRNA. In contrast, in the rat, P1 was used more predominantly in both fetal and adult liver. Exposure of fetal rats to the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone caused suppression of P2 while enhancing hepatic expression of transcripts from P1. This was associated with increased expression of erythropoietin and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, which are key HNF4-alpha targets in the liver. Unlike liver, the kidney and stomach used promoters more selectively, so that only P1-derived isoforms were detected in fetal and adult kidneys in mice or rats, whereas the stomach in both species expressed P2-derived transcripts exclusively. No significant HNF4-alpha mRNA was detected in the spleen. These data reveal striking developmental and tissue-specific variation in expression of HNF4-alpha, and indicate that this can be influenced by environmental factors (such as exposure to glucocorticoid excess), with potential pathophysiological consequences.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha isoforms originated from the P1 promoter are expressed in human pancreatic beta-cells and exhibit stronger transcriptional potentials than P2 promoter-driven isoforms.Endocrinology. 2003 May;144(5):1686-94. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-0024. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12697672
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α regulates the expression of the murine pyruvate carboxylase gene through the HNF4-specific binding motif in its proximal promoter.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1829(10):987-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23665043
-
Prenatal programming of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in the rat: A key mechanism in the 'foetal origins of hyperglycaemia'?Diabetologia. 2006 Jun;49(6):1412-20. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0188-5. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Diabetologia. 2006. PMID: 16570165
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan 7;20(1):22-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24415854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of Cell Identity by the Nuclear Receptor HNF4 in Organ Pathophysiology.Cells. 2020 Sep 28;9(10):2185. doi: 10.3390/cells9102185. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32998360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Effects of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Isoforms on Tumor Growth and T-Cell Factor 4/AP-1 Interactions in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;35(20):3471-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00030-15. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26240283 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin attenuates angiotensin II-induced TGFβ1 expression by targeting hepatocyte nuclear factor-4-α.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;175(8):1217-1229. doi: 10.1111/bph.13753. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28230250 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of hepatic nuclear factor-4α binding to the Stim1 promoter contributes to high glucose-induced upregulation of STIM1 expression in glomerular mesangial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):F1135-45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00563.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25786776 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α and cancer-related cell signaling pathways: a promising insight into cancer treatment.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Jan;53(1):8-18. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-00551-1. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33462379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptor HNF4A transrepresses CLOCK:BMAL1 and modulates tissue-specific circadian networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 26;115(52):E12305-E12312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816411115. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30530698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Briancon N.; Bailly A.; Clotman F.; Jacquemin P.; Lemaigre F. P.; Weiss M. C. Expression of the alpha7 isoform of hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 4 is activated by HNF6/OC-2 and HNF1 and repressed by HNF4alpha1 in the liver. J. Biol. Chem. 279:33398–33408; 2004. - PubMed
-
- Chen W. S.; Manova K.; Weinstein D. C.; Duncan S. A.; Plump A. S.; Prezioso V. R.; Bachvarova R. F.; Darnell J. E. Jr. Disruption of the HNF-4 gene, expressed in visceral endoderm, leads to cell death in embryonic ectoderm and impaired gastrulation of mouse embryos. Genes Dev. 8:2466–2477; 1994. - PubMed
-
- Consoli A.; Nurjhan N. Contribution of gluconeogenesis to overall glucose output in diabetic and nondiabetic men. Ann. Med. 22:191–195; 1990. - PubMed
-
- Dame C.; Fahnenstich H.; Freitag P.; Hofmann D.; Abdul-Nour T.; Bartmann P.; Fandrey J. Erythropoietin mRNA expression in human fetal and neonatal tissue. Blood 92:3218–3225; 1998. - PubMed
-
- Duncan S. A.; Nagy A.; Chan W. Murine gastrulation requires HNF-4 regulated gene expression in the visceral endoderm: Tetraploid rescue of Hnf-4(-/-) embryos. Development 124:279–287; 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
