The role of prostaglandin E2 (PGE 2) in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated colitis-associated neoplasia
- PMID: 20637112
- PMCID: PMC2912804
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-82
The role of prostaglandin E2 (PGE 2) in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated colitis-associated neoplasia
Abstract
Background: We have previously found that TLR4-deficient (TLR4-/-) mice demonstrate decreased expression of mucosal PGE 2 and are protected against colitis-associated neoplasia. However, it is still unclear whether PGE 2 is the central factor downstream of TLR4 signaling that promotes intestinal tumorigenesis. To further elucidate critical downstream pathways involving TLR4-mediated intestinal tumorigenesis, we examined the effects of exogenously administered PGE 2 in TLR4-/- mice to see if PGE 2 bypasses the protection from colitis-associated tumorigenesis.
Method: Mouse colitis-associated neoplasia was induced by azoxymethane (AOM) injection followed by two cycles of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) treatment. Two different doses of PGE 2 (high dose group, 200 microg, n = 8; and low dose group, 100 microg, n = 6) were administered daily during recovery period of colitis by gavage feeding. Another group was given PGE 2 during DSS treatment (200 microg, n = 5). Inflammation and dysplasia were assessed histologically. Mucosal Cox-2 and amphiregulin (AR) expression, prostanoid synthesis, and EGFR activation were analyzed.
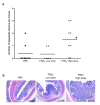
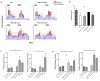
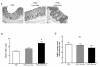
Results: In control mice treated with PBS, the average number of tumors was greater in WT mice (n = 13) than in TLR4-/- mice (n = 7). High dose but not low dose PGE 2 treatment caused an increase in epithelial proliferation. 28.6% of PBS-treated TLR4-/- mice developed dysplasia (tumors/animal: 0.4 +/- 0.2). By contrast, 75.0% (tumors/animal: 1.5 +/- 1.2, P < 0.05) of the high dose group and 33.3% (tumors/animal: 0.3 +/- 0.5) of the low dose group developed dysplasia in TLR4-/- mice. Tumor size was also increased by high dose PGE 2 treatment. Endogenous prostanoid synthesis was differentially affected by PGE 2 treatment during acute and recovery phases of colitis. Exogenous administration of PGE 2 increased colitis-associated tumorigenesis but this only occurred during the recovery phase. Lastly, PGE 2 treatment increased mucosal expression of AR and Cox-2, thus inducing EGFR activation and forming a positive feedback mechanism to amplify mucosal Cox-2.
Conclusions: These results highlight the importance of PGE 2 as a central downstream molecule involving TLR4-mediated intestinal tumorigenesis.
Figures

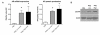

Similar articles
-
A novel Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist antibody ameliorates inflammation but impairs mucosal healing in murine colitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Jun;296(6):G1167-79. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90496.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19359427 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 differentially regulates epidermal growth factor-related growth factors in response to intestinal mucosal injury.Lab Invest. 2010 Sep;90(9):1295-305. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.100. Epub 2010 May 24. Lab Invest. 2010. PMID: 20498653 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of epithelial TLR4 augments inflammatory responses to mucosal injury and drives colitis-associated tumorigenesis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Jul;17(7):1464-73. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21527. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011. PMID: 21674704 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune signaling by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) shapes the inflammatory microenvironment in colitis-associated tumors.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009 Jul;15(7):997-1006. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20880. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. PMID: 19229991 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 signaling in the development of colitis-associated cancer and its possible interplay with microRNA-155.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Sep 3;19(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00771-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34479599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TLR4 activates the β-catenin pathway to cause intestinal neoplasia.PLoS One. 2013 May 14;8(5):e63298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063298. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691015 Free PMC article.
-
Human intestinal epithelial cells express interleukin-10 through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated epithelial-macrophage crosstalk.J Innate Immun. 2015;7(1):87-101. doi: 10.1159/000365417. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Innate Immun. 2015. PMID: 25171731 Free PMC article.
-
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway Targeting TNF-α and Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 Expression in Colonic Mucosa during Ulcerative Colitis and Colitis Associated Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:7353252. doi: 10.1155/2017/7353252. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28408791 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors (TLRs): An old family of immune receptors with a new face in cancer pathogenesis.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jan;25(2):639-651. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16214. Epub 2020 Dec 18. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33336901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of PGE2 in intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015 Jan-Mar;116-117:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015. PMID: 25460828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujiwara I, Yashiro M, Kubo N, Maeda K, Hirakawa K. Ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer is frequently associated with the microsatellite instability pathway. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum. 2008;51(9):1387–1394. - PubMed
-
- Morita H, Nakanishi K, Dohi T, Yasugi E, Oshima M. Phospholipid turnover in the inflamed intestinal mucosa: Arachidonic acid-rich phosphatidyl/plasmenyl-ethanolamine in the mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Gastroenterology. 1999;34(1):46–53. doi: 10.1007/s005350050215. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

