Eph/ephrin interactions modulate vascular sympathetic innervation
- PMID: 20637710
- PMCID: PMC2976839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.06.004
Eph/ephrin interactions modulate vascular sympathetic innervation
Abstract
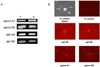
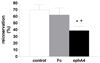
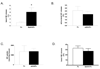
Ephs and ephrins are membrane-bound proteins that interact to modulate axon growth and neuronal function. We tested the hypothesis that eph/ephrin interactions affected the growth and function of vascular sympathetic innervation. Using RT-PCR analyses, we detected both classes of ephs (A and B) and both classes of ephrins (A and B) in sympathetic ganglia from neonatal and adult rats. Both classes of ephs (A and B) and both classes of ephrins (A and B) bound to the cell bodies and neurites of dissociated postganglionic sympathetic neurons. Messenger RNAs encoding for both classes of ephs (A and B) and both classes of ephrins (A and B) were also detected in sympathetically innervated arteries from neonatal and adult rats. These data suggest that ephrins/ephs on nerve fibers of postganglionic sympathetic neurons could interact with ephs/ephrins on cells in innervated arteries. We found that ephA4 reduced reinnervation of denervated femoral arteries. Reinnervation in the presence of ephA4-Fc (38.9±6.6%) was significantly less than that in the presence of IgG-Fc (62±10%; n=5; p<0.05; one-tailed unpaired t-test). These data indicate that eph/ephrin interactions modulated the growth of vascular sympathetic innervation. We also found that ephA4 increased basal release of norepinephrine from nerve terminals of isolated tail arteries. These data indicate that eph/ephrin interactions affect the growth and function of vascular sympathetic innervation.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disruption of ephrin B/Eph B interaction results in abnormal cochlear innervation patterns.Laryngoscope. 2011 Jul;121(7):1541-7. doi: 10.1002/lary.21861. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Laryngoscope. 2011. PMID: 21647913
-
Ephrins and Ephs in cochlear innervation and implications for advancing cochlear implant function.Laryngoscope. 2015 May;125(5):1189-97. doi: 10.1002/lary.25066. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Laryngoscope. 2015. PMID: 25533791
-
Interaxonal Eph-ephrin signaling may mediate sorting of olfactory sensory axons in Manduca sexta.J Neurosci. 2003 Dec 17;23(37):11523-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-37-11523.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14684856 Free PMC article.
-
Ephrin-Eph signaling usage by a variety of viruses.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105038. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105038. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32565311 Review.
-
Eph and ephrin signaling: lessons learned from spinal motor neurons.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Feb;23(1):83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.10.016. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22040916 Review.
Cited by
-
A large-scale genome-wide study of gene-sleep duration interactions for blood pressure in 811,405 individuals from diverse populations.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Aug;30(8):3660-3672. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-02954-w. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40181193
-
Ret is a multifunctional coreceptor that integrates diffusible- and contact-axon guidance signals.Cell. 2012 Feb 3;148(3):568-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.024. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22304922 Free PMC article.
-
Guidance Molecules in Vascular Smooth Muscle.Front Physiol. 2018 Sep 19;9:1311. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01311. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30283356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Study of Gene-Sleep Duration Interactions for Blood Pressure in 811,405 Individuals from Diverse Populations.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 17:rs.3.rs-4163414. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4163414/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Aug;30(8):3660-3672. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-02954-w. PMID: 39070651 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Ephrin ligands and Eph receptors contribution to hematopoiesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Sep;74(18):3377-3394. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2566-1. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28589441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carter AG, Regehr WG. Quantal events shape cerebellar interneuron firing. Nat. Neurosci. 2002;5:1309–1318. - PubMed
-
- Damon DH. NGF-independent survival of postganglionic sympathetic neurons in neuronal-vascular smooth muscle cocultures. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001;280:1722–1728. - PubMed
-
- Damon DH. TH and NPY in sympathetic neurovascular cultures: Role of LIF and NT-3. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008;294:C306–C312. - PubMed
-
- Damon DH, teRiele JA, Marko SB. Vascular-derived artemin: a determinant of vascular sympathetic innervation? Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007;293:H266–H273. - PubMed
-
- Davis S, Gale NW, Aldrich TH, Maisonpierre PC, Lhotak V, Pawson T, Goldfarb M, Yancopoulos GD. Ligands for EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinases that require membrane attachment or clustering for activity. Science. 1994;266:816–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

