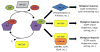
Models for the functions of Arf GAPs
- PMID: 20637885
- PMCID: PMC2976832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.07.002
Models for the functions of Arf GAPs
Abstract
Arf GAPs (ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating proteins) are essential components of Arf (ADP-ribosylation factor) signaling pathways. Arf GAPs stimulate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP to transition Arf from the active, GTP bound, state to the inactive, GDP bound, state. Based on this activity, Arf GAPs were initially proposed to function primarily or exclusively as terminators of Arf signaling. Further studies of Arf GAPs have revealed that they also function as effectors of Arf signaling in at least a few steps or processes in which Arfs are not directly involved. In this review we discuss the non-canonical functions of Arf GAPs and address several key questions in the field, including: whether (1) Arf GAPs are terminators or effectors of Arf signaling, (2) Arf GAPs positively or negatively regulate COPI assembly, (3) Arf GAPs are involved in vesicle fission, and (4) Arf GAPs regulate vesicle uncoating.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kahn RA, Gilman AG. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:7906–11. - PubMed
-
- Cukierman E, Huber I, Rotman M, Cassel D. The ARF1 GTPase-activating protein: zinc finger motif and Golgi complex localization. Science. 1995;270:1999–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

