Mental motor imagery indexes pain: the hand laterality task
- PMID: 20638306
- PMCID: PMC2958243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2010.04.001
Mental motor imagery indexes pain: the hand laterality task
Abstract
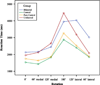
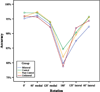
Mental motor imagery is subserved by the same cognitive systems that underlie action. In turn, action is informed by the anticipated sensory consequences of movement, including pain. In light of these considerations, one would predict that motor imagery would provide a useful measure pain-related functional interference. We report a study in which 19 patients with chronic musculoskeletal or radiculopathic arm or shoulder pain, 24 subjects with chronic pain not involving the arm/shoulder and 41 normal controls were asked to indicate if a line drawing was a right or left hand. Previous work demonstrated that this task is performed by mental rotation of the subject's hand to match the stimulus. Relative to normal and pain control subjects, arm/shoulder pain subjects were significantly slower for stimuli that required greater amplitude rotations. For the arm/shoulder pain subjects only there was a correlation between degree of slowing and the rating of severity of pain with movement but not the non-specific pain rating. The hand laterality task may supplement the assessment of subjects with chronic arm/shoulder pain.
Copyright © 2010 European Federation of International Association for the Study of Pain Chapters. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mental motor imagery and chronic pain: the foot laterality task.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2010 Jul;16(4):603-12. doi: 10.1017/S1355617710000299. Epub 2010 Apr 12. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2010. PMID: 20380787 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term adaptation to neck/shoulder pain and perceptual performance in a hand laterality motor imagery test.Perception. 2010;39(1):119-30. doi: 10.1068/p6418. Perception. 2010. PMID: 20301852
-
Action observation improves motor imagery: specific interactions between simulative processes.Exp Brain Res. 2009 Oct;199(1):71-81. doi: 10.1007/s00221-009-1974-3. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Exp Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19690843
-
Neural topography and content of movement representations.J Cogn Neurosci. 2005 Jan;17(1):97-112. doi: 10.1162/0898929052880039. J Cogn Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15701242
-
The effects of healthy aging on mental imagery as revealed by egocentric and allocentric mental spatial transformations.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2013 May;143(1):146-56. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2013.02.014. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23562849
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of the gaze direction recognition task for chronic neck pain and cervical range of motion: a randomized controlled pilot study.Rehabil Res Pract. 2012;2012:570387. doi: 10.1155/2012/570387. Epub 2012 May 7. Rehabil Res Pract. 2012. PMID: 22645685 Free PMC article.
-
Mental rotation of hands and objects in ageing and Parkinson's disease: differentiating motor imagery and visuospatial ability.Exp Brain Res. 2022 Aug;240(7-8):1991-2004. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06389-5. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35680657 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomically plausible illusory posture affects mental rotation of body parts.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2013 Mar;13(1):197-209. doi: 10.3758/s13415-012-0120-z. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22993114
-
When the left hand does not know what the left hand is doing: response mode affects mental rotation of hands.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Jul;228(1):87-95. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3540-2. Epub 2013 May 17. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23681291
-
Cognitive Training Improves Disconnected Limbs' Mental Representation and Peripersonal Space after Spinal Cord Injury.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Sep 12;18(18):9589. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189589. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34574514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blakemore SJ, Frith CD, Wolpert DM. Spatio-temporal prediction modulates the perception of self-produced stimuli. J Cogn Neurosci. 1999 Sep;11(5):551–559. - PubMed
-
- Cleeland CS, Gonin R, Hatfield AK, Edmonson JH, Blum RH, Stewart JA, Pandya KJ. Pain and its treatment in outpatients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1994;330(9):592–596. - PubMed
-
- Coslett HB. Evidence for a disturbance of the body schema in neglect. Brain Cogn. 1998 Aug;37(3):527–544. - PubMed
-
- Coslett HB, Medina J, Kliot D, Burkey A. Mental Motor Imagery and Chronic Pain: The Foot Laterality Task. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. In press. - PubMed
-
- Daly AE, Bialocerkowski AE. Does evidence support physiotherapy management of adult Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type One? A systematic review. European Journal of Pain. 2009;13:339–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

