Janus kinase 2 is required for the initiation but not maintenance of prolactin-induced mammary cancer
- PMID: 20639901
- PMCID: PMC2997721
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.274
Janus kinase 2 is required for the initiation but not maintenance of prolactin-induced mammary cancer
Abstract
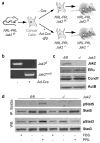
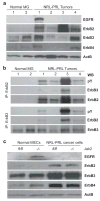
The prolactin receptor (PRLR), its associated Janus kinase 2 (Jak2) and the signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (Stat5) are essential for normal mammary gland development. Owing to the upregulation of the PRLR and the local synthesis of its ligand in neoplastic cells, it has been proposed that PRL can act as a local growth factor in human breast cancers. This notion is supported by experimental evidence in transgenic mice, which showed that the mammary-specific expression of PRL contributes to carcinogenesis in vivo. To assess the importance of Jak2/Stat5 signaling during mammary cancer initiation and progression, we generated a PRL-induced mammary cancer model that allows the functional ablation of the Jak2 gene in the mammary epithelium before and after neoplastic transformation. Collectively, the results of this study show that the functional ablation of Jak2 protects against the onset of PRL-induced mammary tumorigenesis, suggesting that targeting this kinase is a relevant strategy for mammary cancer prevention. Surprisingly, Jak2 deficiency did not affect the growth and survival of PRL-induced mammary cancer cells in culture and in vivo. Consequently, Jak2 cannot be a sole therapeutic target to treat the established disease. PRL-induced mammary cancers exhibited an upregulation of ErbB2 and other ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases that may supersede the functionality of PRLR signaling through Jak2.
Figures




References
-
- aoui-Jamali MA, Song DJ, Benlimame N, Yen L, Deng X, Hernandez-Perez M, et al. Regulation of multiple tumor microenvironment markers by overexpression of single or paired combinations of ErbB receptors. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3764–3774. - PubMed
-
- Boulanger CA, Wagner KU, Smith GH. Parity-induced mouse mammary epithelial cells are pluripotent, self-renewing and sensitive to TGF-beta1 expression. Oncogene. 2005;24:552–560. - PubMed
-
- Brockman JL, Schroeder MD, Schuler LA. PRL activates the cyclin D1 promoter via the Jak2/Stat pathway. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:774–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

