Safety, tolerability, and immunologic effects of a food allergy herbal formula in food allergic individuals: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, phase 1 study
- PMID: 20642207
- PMCID: PMC3026589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anai.2010.05.005
Safety, tolerability, and immunologic effects of a food allergy herbal formula in food allergic individuals: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, phase 1 study
Abstract
Background: Food allergy is a common and serious health problem. A new herbal product, called food allergy herbal formula 2 (FAHF-2), has been demonstrated to have a high safety profile and potent long-term efficacy in a murine model of peanut-induced anaphylaxis.
Objective: To evaluate the safety and tolerability of FAHF-2 in patients with food allergy.
Methods: In this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, phase 1 trial, patients received 1 of 3 doses of FAHF-2 or placebo: 2.2 g (4 tablets), 3.3 g (6 tablets), or 6.6 g (12 tablets) 3 times a day for 7 days. Four active and 2 placebo patients were treated at each dose level. Vital signs, physical examination results, laboratory data, pulmonary function test results, and electrocardiogram data were monitored. Immunomodulatory studies were also performed.
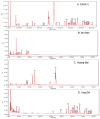
Results: Nineteen food allergic participants were included in the study. Two patients (1 in the FAHF-2 group and 1 in the placebo group) reported mild gastrointestinal symptoms. One patient withdrew from the study because of an allergic reaction that was unlikely related to the study medication. No significant differences were found in vital signs, physical examination results, laboratory data, pulmonary function test results, and electrocardiogram data obtained before and after treatment visits. Significantly decreased interleukin (IL) 5 levels were found in the active treatment group after 7 days. In vitro studies of peripheral blood mononuclear cells cultured with FAHF-2 also demonstrated a significant decrease in IL-5 and an increase in culture supernatant interferon gamma and IL-10 levels.
Conclusions: FAHF-2 appeared to be safe and well tolerated in patients with food allergy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00602160.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
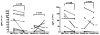
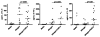
Similar articles
-
Safety, clinical, and immunologic efficacy of a Chinese herbal medicine (Food Allergy Herbal Formula-2) for food allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Oct;136(4):962-970.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.04.029. Epub 2015 Jun 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26044855 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical safety of Food Allergy Herbal Formula-2 (FAHF-2) and inhibitory effect on basophils from patients with food allergy: Extended phase I study.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Dec;128(6):1259-1265.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.06.015. Epub 2011 Jul 26. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21794906 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Food allergy herbal formula 2 protection against peanut anaphylactic reaction is via inhibition of mast cells and basophils.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Dec;126(6):1208-17.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.09.013. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21134573 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal therapy for the treatment of food allergy.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012 Aug;12(4):332-8. doi: 10.1007/s11882-012-0265-4. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012. PMID: 22581122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Food allergy prevalence: new possibilities for therapy and prevention.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2012 Dec;162(23-24):519-24. doi: 10.1007/s10354-012-0159-z. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2012. PMID: 23188465 Review.
Cited by
-
Pepsinized cashew proteins are hypoallergenic and immunogenic and provide effective immunotherapy in mice with cashew allergy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Sep;130(3):716-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.044. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22795369 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory Effects of Ganoderma lucidum Triterpenoid in Human Crohn's Disease Associated with Downregulation of NF-κB Signaling.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Aug;21(8):1918-25. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000439. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 25993687 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Anti-IgE in Food Allergy Therapy.Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2014 Jun 1;1(2):145-156. doi: 10.1007/s40521-014-0015-z. Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2014. PMID: 25419508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Food allergy diagnosis and therapy: where are we now?Immunotherapy. 2013 Sep;5(9):931-44. doi: 10.2217/imt.13.93. Immunotherapy. 2013. PMID: 23998729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Shellfish Allergy Therapy: From Current Approaches to Future Strategies.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Jul 16;68(1):65. doi: 10.1007/s12016-025-09077-8. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40668267 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(2 suppl):S470–S475. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Sampson HA. Food anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:651–660. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001–2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1016–1018. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:191–193. - PubMed
-
- Guo R, Pittler MH, Ernst E. Herbal medicines for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a systematic review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007;99:483–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

