Safety, tolerability, and immunologic effects of a food allergy herbal formula in food allergic individuals: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, phase 1 study
- PMID: 20642207
- PMCID: PMC3026589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anai.2010.05.005
Safety, tolerability, and immunologic effects of a food allergy herbal formula in food allergic individuals: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, phase 1 study
Abstract
Background: Food allergy is a common and serious health problem. A new herbal product, called food allergy herbal formula 2 (FAHF-2), has been demonstrated to have a high safety profile and potent long-term efficacy in a murine model of peanut-induced anaphylaxis.
Objective: To evaluate the safety and tolerability of FAHF-2 in patients with food allergy.
Methods: In this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, dose escalation, phase 1 trial, patients received 1 of 3 doses of FAHF-2 or placebo: 2.2 g (4 tablets), 3.3 g (6 tablets), or 6.6 g (12 tablets) 3 times a day for 7 days. Four active and 2 placebo patients were treated at each dose level. Vital signs, physical examination results, laboratory data, pulmonary function test results, and electrocardiogram data were monitored. Immunomodulatory studies were also performed.
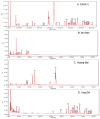
Results: Nineteen food allergic participants were included in the study. Two patients (1 in the FAHF-2 group and 1 in the placebo group) reported mild gastrointestinal symptoms. One patient withdrew from the study because of an allergic reaction that was unlikely related to the study medication. No significant differences were found in vital signs, physical examination results, laboratory data, pulmonary function test results, and electrocardiogram data obtained before and after treatment visits. Significantly decreased interleukin (IL) 5 levels were found in the active treatment group after 7 days. In vitro studies of peripheral blood mononuclear cells cultured with FAHF-2 also demonstrated a significant decrease in IL-5 and an increase in culture supernatant interferon gamma and IL-10 levels.
Conclusions: FAHF-2 appeared to be safe and well tolerated in patients with food allergy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00602160.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
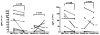
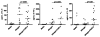
References
-
- Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(2 suppl):S470–S475. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Sampson HA. Food anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:651–660. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001–2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1016–1018. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:191–193. - PubMed
-
- Guo R, Pittler MH, Ernst E. Herbal medicines for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a systematic review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007;99:483–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

