Effect of hydrochlorothiazide on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat, a non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase
- PMID: 20642548
- PMCID: PMC2909808
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03667.x
Effect of hydrochlorothiazide on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat, a non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase
Abstract
What is already known about this subject: Hyperuricaemia and gout frequently coexist with cardiovascular disorders such as hypertension and heart failure. The use of diuretics has been re-established as a first-line treatment for patients with hypertension and the effects of diuretics on serum uric acid may diminish the urate-lowering effects of febuxostat, a novel, potent, non-purine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase.
What this study adds: Co-administration of febuxostat 80 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg had no effect on the pharmacokinetics and did not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacodynamics of febuxostat. Dose adjustment for febuxostat is not necessary when it is administered with hydrochlorothiazide.
Aim: This study examined the effect of co-administration of febuxostat, an investigational urate lowering therapy, and hydrochlorothiazide on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of febuxostat.
Methods: Healthy subjects (36 healthy men and women) received single doses of febuxostat 80 mg alone and febuxostat 80 mg + hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg, separated by 7 days in an open-label, randomized, crossover fashion. Plasma concentrations of febuxostat and urinary and serum concentrations of uric acid were assessed.
Results: Mean febuxostat C(max), AUC((0-t)), AUC((0-infinity)), t(1/2,z), CL/F and V(ss)/F values for regimens co-administration/febuxostat alone were 2.9/2.9 microg ml(-1), 9.3/9.1 microg ml(-1) h, 9.6/9.3 microg ml(-1) h, 6.5/6.1 h, 8.8/9.3 l h(-1) and 45/44 l, respectively. Geometric mean ratios (co-administration : febuxostat alone) and their 90% confidence intervals for febuxostat plasma C(max), AUC((0-t)), and AUC((0-infinity)) were 1.00 (0.86, 1.17), 1.03 (0.98, 1.09), and 1.04 (0.98, 1.10), respectively; all of the 90% CIs were within the no effect range of 0.8 to 1.25. Serum uric acid C(mean,24h), C(mean,48h) and CL(R) for both regimens co-administration/febuxostat alone were 216/203 micromol l(-1), 218/202 micromol l(-1) and 9.1/10.1 ml min(-1), respectively. Although serum uric acid C(mean,24h) and C(mean,48h) values were higher and CL(R) values lower after co-administration compared with dosing of febuxostat alone, with the differences being statistically significant (P < 0.003), none of the differences (6.5%-9.5%) was considered clinically significant.
Conclusion: Dose adjustment for febuxostat is not necessary when it is administered with hydrochlorothiazide.
Figures
References
-
- Schlesinger N. Management of acute and chronic gouty arthritis: present state-of-the-art. Drugs. 2004;64:2399–416. - PubMed
-
- Takano Y, Hase-Aoki K, Horiuchi H, Zhao L, Kasahara Y, Kondo S, Becker MA. Selectivity of febuxostat, a novel non-purine inhibitor of xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase. Life Sci. 2005;76:1835–47. - PubMed
-
- Sarawate CA, Patel PA, Schumacher HR, Yang W, Brewer KK, Bakst AW. Serum urate levels and gout flares: analysis from managed care data. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006;12:61–5. - PubMed
-
- Becker M, Schumacher HR, Jr, Wortmann R, MacDonald P, Eustace D, Palo W, Streit J, Joseph-Ridge N. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2450–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

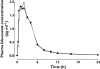
 ); Febuxostat + hydrochlorthiazide…
); Febuxostat + hydrochlorthiazide…  )
)