Protein determinants of SNARE-mediated lipid mixing
- PMID: 20643074
- PMCID: PMC2905075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.04.060
Protein determinants of SNARE-mediated lipid mixing
Abstract
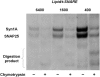
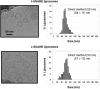
Soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE)-mediated lipid mixing can be efficiently recapitulated in vitro by the incorporation of purified vesicle membrane (-v) SNARE and target membrane (t-) SNARE proteins into separate liposome populations. Despite the strong correlation between the observed activities in this system and the known SNARE physiology, some recent works have suggested that SNARE-mediated lipid mixing may be limited to circumstances where membrane defects arise from artifactual reconstitution conditions (such as nonphysiological high-protein concentrations or unrealistically small liposome populations). Here, we show that the previously published strategies used to reconstitute SNAREs into liposomes do not significantly affect either the physical parameters of the proteoliposomes or the ability of SNAREs to drive lipid mixing in vitro. The surface density of SNARE proteins turns out to be the most critical parameter, which controls both the rate and the extent of SNARE-mediated liposome fusion. In addition, the specific activity of the t-SNARE complex is significantly influenced by expression and reconstitution protocols, such that we only observe optimal lipid mixing when the t-SNARE proteins are coexpressed before purification.
Copyright (c) 2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reconstituted Proteoliposome Fusion Mediated by Yeast SNARE-Family Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1860:303-322. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8760-3_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30317514
-
Studying protein-reconstituted proteoliposome fusion with content indicators in vitro.Bioessays. 2013 Jul;35(7):658-65. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300010. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 23625805 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-directed molecular assembly of the neuronal SNARE complex.J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Jan;15(1):31-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01152.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20716122 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane fusion in cells: molecular machinery and mechanisms.J Cell Mol Med. 2006 Apr-Jun;10(2):423-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00409.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16796809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards reconstitution of membrane fusion mediated by SNAREs and other synaptic proteins.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;50(3):231-41. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1023252. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25788028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic roles of Synaptotagmin-1 and complexin in calcium-regulated neuronal exocytosis.Elife. 2020 May 13;9:e54506. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54506. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32401194 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Lipids and Divalent Cations in Membrane Fusion Mediated by the Heptad Repeat Domain 1 of Mitofusin.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 2;13(9):1341. doi: 10.3390/biom13091341. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759741 Free PMC article.
-
The Get1/2 insertase forms a channel to mediate the insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the ER.Cell Rep. 2023 Jan 31;42(1):111921. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111921. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36640319 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and characterization of SNARE-containing nanodiscs and direct study of cargo release through fusion pores.Nat Protoc. 2013 May;8(5):935-48. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.048. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 23598444
-
Biomimetic membrane in a microfluidic chip for the electrical and optical monitoring of biological reactions.Nat Protoc. 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1038/s41596-025-01171-7. Online ahead of print. Nat Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40461799 Review.
References
-
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S.W., Rothman J.E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993;362:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T. Structure and function of SNARE and SNARE-interacting proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2005;38:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Jackson M.B., Chapman E.R. Fusion pores and fusion machines in Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2006;35:135–160. - PubMed
-
- Jahn R., Scheller R.H. SNAREs—engines for membrane fusion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:631–643. - PubMed
-
- Hanson P.I., Roth R., Heuser J.E. Structure and conformational changes in NSF and its membrane receptor complexes visualized by quick-freeze/deep-etch electron microscopy. Cell. 1997;90:523–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

