Pax2 coordinates epithelial morphogenesis and cell fate in the inner ear
- PMID: 20643116
- PMCID: PMC2946559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.07.007
Pax2 coordinates epithelial morphogenesis and cell fate in the inner ear
Abstract
Crucial components of the vertebrate eye, ear and nose develop from discrete patches of surface epithelium, called placodes, which fold into spheroids and undergo complex morphogenesis. Little is known about how the changes in cell and tissue shapes are coordinated with the acquisition of cell fates. Here we explore whether these processes are regulated by common transcriptional mechanisms in the developing ear. After specification, inner ear precursors elongate to form the placode, which invaginates and is transformed into the complex structure of the adult ear. We show that the transcription factor Pax2 plays a key role in coordinating otic fate and placode morphogenesis, but appears to regulate each process independently. In the absence of Pax2, otic progenitors not only lose otic marker expression, but also fail to elongate due to the loss of apically localised N-cadherin and N-CAM. In the absence of either N-cadherin or N-CAM otic cells lose apical cell-cell contact and their epithelial shape. While misexpression of Pax2 leads to ectopic activation of both adhesion molecules, it is not sufficient to confer otic identity. These observations suggest that Pax2 controls cell shape independently from cell identity and thus acts as coordinator for these processes.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
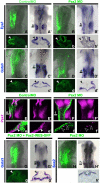



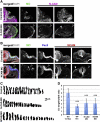

Similar articles
-
Eya1 regulates the growth of otic epithelium and interacts with Pax2 during the development of all sensory areas in the inner ear.Dev Biol. 2006 Oct 15;298(2):430-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.049. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16916509 Free PMC article.
-
Pax2 expression patterns in the developing chick inner ear.Gene Expr Patterns. 2005 Aug;5(6):763-73. doi: 10.1016/j.modgep.2005.04.007. Gene Expr Patterns. 2005. PMID: 15979948
-
Wnt signals mediate a fate decision between otic placode and epidermis.Development. 2006 Mar;133(5):865-75. doi: 10.1242/dev.02271. Epub 2006 Feb 1. Development. 2006. PMID: 16452098
-
Induction of the inner ear: stepwise specification of otic fate from multipotent progenitors.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.018. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23194992 Review.
-
A symphony of inner ear developmental control genes.BMC Genet. 2010 Jul 16;11:68. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-11-68. BMC Genet. 2010. PMID: 20637105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pax2 and Pax8 cooperate in mouse inner ear morphogenesis and innervation.BMC Dev Biol. 2010 Aug 20;10:89. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-89. BMC Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20727173 Free PMC article.
-
PAX2 induces vascular-like structures in normal ovarian cells and ovarian cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun;23(6):412. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11339. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35601066 Free PMC article.
-
Deterioration of the Medial Olivocochlear Efferent System Accelerates Age-Related Hearing Loss in Pax2-Isl1 Transgenic Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2368-83. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9215-1. Epub 2015 May 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25990412
-
Comparative assessment of Fgf's diverse roles in inner ear development: A zebrafish perspective.Dev Dyn. 2021 Nov;250(11):1524-1551. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.343. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Dev Dyn. 2021. PMID: 33830554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone demethylase KDM4B regulates otic vesicle invagination via epigenetic control of Dlx3 expression.J Cell Biol. 2015 Nov 23;211(4):815-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201503071. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26598618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey A.P., Bhattacharyya S., Bronner-Fraser M., Streit A. Lens specification is the ground state of all sensory placodes, from which FGF promotes olfactory identity. Dev. Cell. 2006;11:505–517. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft M., Bellairs R. Placodes of the chick embryo studied by SEM. Anat. Embryol. (Berl). 1977;151:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Barembaum M., Bronner-Fraser M. Spalt mediates invagination and otic placode gene expression in cranial ectoderm. Development. 2007;134:3805–3814. - PubMed
-
- Barrionuevo F., Naumann A., Bagheri-Fam S., Speth V., Taketo M.M., Scherer G., Neubüser A. Sox9 is required for invagination of the otic placode in mice. Dev. Biol. 2008;317:213–224. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard M., Pfeffer P., Busslinger M. Functional equivalence of the transcription factors Pax2 and Pax5 in mouse development. Development. 2000;127:3703–3713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

