Can we protect the gut in critical illness? The role of growth factors and other novel approaches
- PMID: 20643306
- PMCID: PMC2908596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2010.04.005
Can we protect the gut in critical illness? The role of growth factors and other novel approaches
Abstract
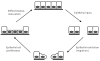
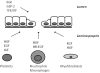
The intestine plays a central role in the pathophysiology of critical illness and is frequently called the "motor" of the systemic inflammatory response. Perturbations to the intestinal barrier can lead to distant organ damage and multiple organ failure. Therefore, identifying ways to preserve intestinal integrity may be of paramount importance. Growth factors and other peptides have emerged as potential tools for modulation of intestinal inflammation and repair due to their roles in cellular proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival. This review examines the involvement of growth factors and other peptides in intestinal epithelial repair during critical illness and their potential use as therapeutic targets.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hassoun HT, Kone BC, Mercer DW, Moody FG, Weisbrodt NW, Moore FA. Post-injury multiple organ failure: the role of the gut. Shock. 2001;15:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Alverdy JC, Laughlin RS, Wu L. Influence of the critically ill state on host-pathogen interactions within the intestine: gut-derived sepsis redefined. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:598–607. - PubMed
-
- Fink MP. Intestinal epithelial hyperpermeability: update on the pathogenesis of gut mucosal barrier dysfunction in critical illness. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2003;9:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Han X, Fink MP, Yang R, Delude RL. Increased iNOS activity is essential for intestinal epithelial tight junction dysfunction in endotoxemic mice. Shock. 2004;21:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Fink MP, Delude RL. Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction: A Unifying Theme to Explain the Pathogenesis of Multiple Organ Dysfunction at the Cellular Level. Crit Care Clin. 2005;21:177–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

