Lung squamous cell carcinoma mRNA expression subtypes are reproducible, clinically important, and correspond to normal cell types
- PMID: 20643781
- PMCID: PMC2953768
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0199
Lung squamous cell carcinoma mRNA expression subtypes are reproducible, clinically important, and correspond to normal cell types
Abstract
Purpose: Lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is clinically and genetically heterogeneous, and current diagnostic practices do not adequately substratify this heterogeneity. A robust, biologically based SCC subclassification may describe this variability and lead to more precise patient prognosis and management. We sought to determine if SCC mRNA expression subtypes exist, are reproducible across multiple patient cohorts, and are clinically relevant.
Experimental design: Subtypes were detected by unsupervised consensus clustering in five published discovery cohorts of mRNA microarrays, totaling 382 SCC patients. An independent validation cohort of 56 SCC patients was collected and assayed by microarrays. A nearest-centroid subtype predictor was built using discovery cohorts. Validation cohort subtypes were predicted and evaluated for confirmation. Subtype survival outcome, clinical covariates, and biological processes were compared by statistical and bioinformatic methods.
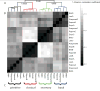
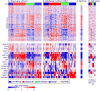
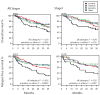
Results: Four lung SCC mRNA expression subtypes, named primitive, classical, secretory, and basal, were detected and independently validated (P < 0.001). The primitive subtype had the worst survival outcome (P < 0.05) and is an independent predictor of survival (P < 0.05). Tumor differentiation and patient sex were associated with subtype. The expression profiles of the subtypes contained distinct biological processes (primitive: proliferation; classical: xenobiotic metabolism; secretory: immune response; basal: cell adhesion) and suggested distinct pharmacologic interventions. Comparison with lung model systems revealed distinct subtype to cell type correspondence.
Conclusions: Lung SCC consists of four mRNA expression subtypes that have different survival outcomes, patient populations, and biological processes. The subtypes stratify patients for more precise prognosis and targeted research.
©2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Koyi H, Hillerdal G, Branden E. A prospective study of a total material of lung cancer from a county in Sweden 1997-1999: gender, symptoms, type, stage, and smoking habits. Lung Cancer. 2002;36:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Visbal AL, Williams BA, Nichols FC, 3rd, et al. Gender differences in non-small-cell lung cancer survival: an analysis of 4,618 patients diagnosed between 1997 and 2002. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78:209–15. discussion 15. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD World Health Organization. Histological typing of lung and pleural tumours. Berlin: Springer; 1999.
-
- Auerbach O, Garfinkel L, Parks VR. Histologic type of lung cancer in relation to smoking habits, year of diagnosis and sites of metastases. Chest. 1975;67:382–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

