Reactive oxygen species, NADPH oxidases, and hypertension
- PMID: 20644010
- PMCID: PMC2947547
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.142422
Reactive oxygen species, NADPH oxidases, and hypertension
Figures

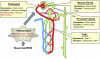

References
-
- Sun C, Sellers KW, Sumners C, Raizada MK. NAD(P)H Oxidase Inhibition Attenuates Neuronal Chronotropic Actions of Angiotensin II. Circ Res. 2005;96:659–666. - PubMed
-
- Ye S, Zhong H, Campese VM. Oxidative Stress Mediates the Stimulation of Sympathetic Nerve Activity in the Phenol Renal Injury Model of Hypertension. Hypertension. 2006;48:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Fujita M, Ando K, Nagae A, Fujita T. Sympathoexcitation by Oxidative Stress in the Brain Mediates Arterial Pressure Elevation in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Hypertension. 2007;50:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Peterson JR, Burmeister MA, Tian X, Zhou Y, Guruju MR, Stupinski JA, Sharma RV, Davisson RL. Genetic Silencing of Nox2 and Nox4 Reveals Differential Roles of These NADPH Oxidase Homologues in the Vasopressor and Dipsogenic Effects of Brain Angiotensin II. Hypertension. 2009;54:1106–1114. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

