AMPK enhances the expression of pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 via PPARalpha, but not PPARgamma, in rat insulinoma cell line INS-1
- PMID: 20644547
- PMCID: PMC4007814
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.78
AMPK enhances the expression of pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 via PPARalpha, but not PPARgamma, in rat insulinoma cell line INS-1
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulates the expression of pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 (PDX-1), a beta-cell-specific transcription factor and whether PPARalpha/gamma is involved in the regulation of pancreatic beta-cell lines after acute stimulation.
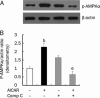
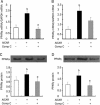
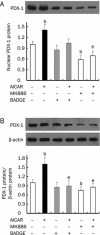
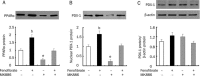
Methods: Rat insulinoma cell line INS-1 was treated with an activator (AICAR) or inhibitor (Compound C) of AMPK as well as inhibitors of PPARs (MK886 to PPARalpha and BADGE to PPARgamma). The mRNA levels of PDX-1, PPARalpha and PPARgamma were measured using real-time RT-PCR, and Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression of these factors.
Results: Activation of AMPK by AICAR induced significantly increased the expression of PDX-1, and this increase was abrogated when AMPK was inactivated by Compound C. Similarly, the expression of PPARalpha and PPARgamma was also increased by AICAR or decreased by Compound C. However AMPK activation did not increase nuclear PDX-1 protein levels when PPARalpha was inhibited. In contrast, AMPK activation still up-regulated PDX-1 protein levels during PPARgamma inhibition. Additionally, PPARalpha activation induced by fenofibrate significantly enhanced nuclear PDX-1 protein expression.
Conclusion: AMPK regulates the expression of PDX-1 at both the transcriptional and protein levels, and PPARalpha may be acutely involved in the regulation of INS-1 cells.
Figures

References
-
- Merrill GF, Kurth EJ, Hardie DG, Winder WW. AICA riboside increases AMP-activated protein kinase, fatty acid oxidation, and glucose uptake in rat muscle. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:E1107–12. - PubMed
-
- Kurth-Kraczek EJ, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ, Winder WW. 5′AMP-activated protein kinase activation causes GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1999;48:1667–71. - PubMed
-
- Ojuka EO, Jones TE, Nolte LA, Chen M, Wamhoff BR, Sturek M, et al. Regulation of GLUT4 biogenesis in muscle: evidence for involvement of AMPK and Ca2+ Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282:E1008–13. - PubMed
-
- Leff T. AMP-activated protein kinase regulates gene expression by direct phosphorylation of nuclear proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:224–7. - PubMed
-
- Saleh MC, Fatehi-Hassanabad Z, Wang R, Nino-Fong R, Wadowska DW, Wright GM, et al. Mutated ATP synthase induces oxidative stress and impaired insulin secretion in beta-cells of female BHE/cdb rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24:392–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

