Ferulic acid inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis by enhancing GABA(B1) receptor expression in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats
- PMID: 20644551
- PMCID: PMC4007809
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.66
Ferulic acid inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis by enhancing GABA(B1) receptor expression in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats
Abstract
Aim: Ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid, FA) provides neuroprotection against apoptosis in a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) model. This study was to further investigate the anti-apoptotic effect of FA during reperfusion after cerebral ischemia.
Methods: Rats were subjected to 90 min of cerebral ischemia followed by 3 or 24 h of reperfusion after which they were sacrificed.
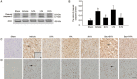
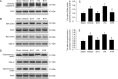
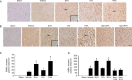
Results: Intravenous FA (100 mg/kg) administered immediately after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) or 2 h after reperfusion effectively abrogated the elevation of postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), nitrotyrosine, and cleaved caspase-3 levels as well as apoptosis in the ischemic cortex at 24 h of reperfusion. FA further inhibited Bax translocation, cytochrome c release, and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase phosphorylation. Moreover, FA enhanced the expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1 (GABA(B1)) in the ischemic cortex at 3 and 24 h of reperfusion. In addition, nitrotyrosine-positive cells colocalized with cleaved caspase-3-positive cells, and phospho-p38 MAP kinase-positive cells colocalized with nitrotyrosine- and Bax-positive cells, indicating a positive relationship among the expression of nitrotyrosine, phospho-p38 MAP kinase, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3. The mutually exclusive expression of GABA(B1) and nitrotyrosine revealed that there is a negative correlation between GABA(B1) and nitrotyrosine expression profiles. Additionally, pretreatment with saclofen, a GABA(B) receptor antagonist, abolished the neuroprotection of FA against nitric oxide (NO)-induced apoptosis.
Conclusion: FA significantly enhances GABA(B1) receptor expression at early reperfusion and thereby provides neuroprotection against p38 MAP kinase-mediated NO-induced apoptosis at 24 h of reperfusion.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ferulic acid provides neuroprotection against oxidative stress-related apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ICAM-1 mRNA expression in rats.Brain Res. 2008 May 13;1209:136-50. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.090. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18400211
-
Ferulic Acid Administered at Various Time Points Protects against Cerebral Infarction by Activating p38 MAPK/p90RSK/CREB/Bcl-2 Anti-Apoptotic Signaling in the Subacute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats.PLoS One. 2016 May 17;11(5):e0155748. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155748. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27187745 Free PMC article.
-
Angelica sinensis Exerts Angiogenic and Anti-apoptotic Effects Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Activating p38MAPK/HIF-1[Formula: see text]/VEGF-A Signaling in Rats.Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(8):1683-1708. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500914. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Am J Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 29121798
-
Neuroprotection of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor agonists via enhancing neuronal nitric oxide synthase (Ser847) phosphorylation through increased neuronal nitric oxide synthase and PSD95 interaction and inhibited protein phosphatase activity in cerebral ischemia.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Oct;86(13):2973-83. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21728. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18512761
-
Recent Advances in Biological Activity, New Formulations and Prodrugs of Ferulic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 28;22(23):12889. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312889. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of GABAB Receptor Suppresses Diabetic Neuropathic Pain through Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway in the Spinal Dorsal Horn.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 10;2018:6016272. doi: 10.1155/2018/6016272. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30647535 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ferulic Acid on Respiratory Metabolism, Oxidative Lesions, and Apoptotic Parameters in Gills and Red Blood Cells of Carp (Cyprinus carpio Var. Jian) Response to Copper.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 4;13(3):314. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030314. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539847 Free PMC article.
-
Date Palm as Source of Nutraceuticals for Health Promotion: a Review.Curr Nutr Rep. 2022 Dec;11(4):574-591. doi: 10.1007/s13668-022-00437-w. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Curr Nutr Rep. 2022. PMID: 36125704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Targets for Modulation of Immune Response and Inflammation in Stroke.Neurochem Res. 2023 Jun;48(6):1663-1690. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03875-2. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36763312 Review.
-
Efficacy of ferulic acid in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke injury in rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1278036. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1278036. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37927604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirino T. Delayed neuronal death. Neuropathology. 2000;20:S95–7. - PubMed
-
- Friedlander RM. Apoptosis and caspases in neurodegenerative diseases. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1365–75. - PubMed
-
- Kermer P, Liman J, Weishaupt JH, Bahr M. Neuronal apoptosis in neurodegenerative diseases: from basic research to clinical application. Neurodegener Dis. 2004;1:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Lin N, Wu B, Qiu Y. Neuroprotective effect of memantine combined with topiramate in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Brain Res. 2009;1282:173–82. - PubMed
-
- Cardenas A, Moro MA, Hurtado O, Leza JC, Lorenzo P, Castrillo A, et al. Implication of glutamate in the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase after oxygen and glucose deprivation in rat forebrain slices. J Neurochem. 2000;74:2041–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

