Epithelial decision makers: in search of the 'epimmunome'
- PMID: 20644571
- PMCID: PMC2950874
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1905
Epithelial decision makers: in search of the 'epimmunome'
Abstract
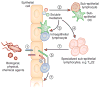
Frequent microbial and nonmicrobial challenges to epithelial cells trigger discrete pathways, promoting molecular changes such as the secretion of specific cytokines and chemokines and alterations to molecules displayed at the epithelial cell surface. In combination, these molecules impose key decisions on innate and adaptive immune cells. Depending on context, those decisions can be as diverse as those imposed by professional antigen-presenting cells, benefiting the host by balancing immune competence with the avoidance of immunopathology. Nonetheless, this potency of epithelial cells is also consistent with the causal contribution of epithelial dysregulation to myriad inflammatory diseases. This pathogenic axis provides an attractive target for tissue-specific clinical manipulation. In this context, a research goal should be to identify all molecules used by epithelial cells to instruct immune cells. We term this the 'epimmunome'.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson G, Jenkinson EJ. Lymphostromal interactions in thymic development and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Thorey IS, et al. The Ca2+-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 are encoded by novel injury-regulated genes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:35818–35825. - PubMed
-
- Ghavami S, et al. S100A8/A9: a Janus-faced molecule in cancer therapy and tumorgenesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009;625:73–83. - PubMed
-
- Bando M, et al. Interleukin-1alpha regulates antimicrobial peptide expression in human keratinocytes. Immunology and Cell Biology. 2007;85:532–537. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JM, Romero MR, Watt FM. Suprabasal integrin expression in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in developmental defects and a phenotype resembling psoriasis. Cell. 1995;83:957–968. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

