Determining vitamin D status: a comparison between commercially available assays
- PMID: 20644628
- PMCID: PMC2903481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011555
Determining vitamin D status: a comparison between commercially available assays
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2010;5(9). doi: 10.1371/annotation/23307aa4-726e-4f11-86c0-8a292be33517
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D is not only important for bone health but can also affect the development of several non-bone diseases. The definition of vitamin D insufficiency by serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D depends on the clinical outcome but might also be a consequence of analytical methods used for the definition. Although numerous 25-hydroxyvitamin D assays are available, their comparability is uncertain. We therefore aim to investigate the precision, accuracy and clinical consequences of differences in performance between three common commercially available assays.
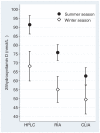
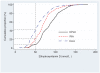
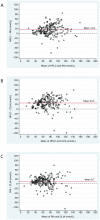
Methodology/principal findings: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels from 204 twins from the Swedish Twin Registry were determined with high-pressure liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry (HPLC-APCI-MS), a radioimmunoassay (RIA) and a chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLIA). High inter-assay disagreement was found. Mean 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were highest for the HPLC-APCI-MS technique (85 nmol/L, 95% CI 81-89), intermediate for RIA (70 nmol/L, 95% CI 66-74) and lowest with CLIA (60 nmol/L, 95% CI 56-64). Using a 50-nmol/L cut-off, 8% of the subjects were insufficient using HPLC-APCI-MS, 22% with RIA and 43% by CLIA. Because of the heritable component of 25-hydroxyvitamin D status, the accuracy of each method could indirectly be assessed by comparison of within-twin pair correlations. The strongest correlation was found for HPLC-APCI-MS (r = 0.7), intermediate for RIA (r = 0.5) and lowest for CLIA (r = 0.4). Regression analyses between the methods revealed a non-uniform variance (p<0.0001) depending on level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
Conclusions/significance: There are substantial inter-assay differences in performance. The most valid method was HPLC-APCI-MS. Calibration between 25-hydroxyvitamin D assays is intricate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dietrich T, Orav EJ, Dawson-Hughes B. Positive association between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and bone mineral density: a population-based study of younger and older adults. Am J Med. 2004;116:634–639. - PubMed
-
- Lips P. Vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism in the elderly: consequences for bone loss and fractures and therapeutic implications. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:477–501. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dietrich T, Orav EJ, Hu FB, Zhang Y, et al. Higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with better lower-extremity function in both active and inactive persons aged > or = 60 y. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:752–758. - PubMed
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D: importance in the prevention of cancers, type 1 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:362–371. - PubMed
-
- Forman JP, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC. Vitamin D intake and risk of incident hypertension: results from three large prospective cohort studies. Hypertension. 2005;46:676–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

