miR-148 regulates Mitf in melanoma cells
- PMID: 20644734
- PMCID: PMC2904378
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011574
miR-148 regulates Mitf in melanoma cells
Abstract
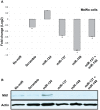
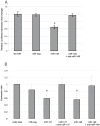
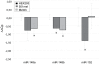
The Microphthalmia associated transcription factor (Mitf) is an important regulator in melanocyte development and has been shown to be involved in melanoma progression. The current model for the role of Mitf in melanoma assumes that the total activity of the protein is tightly regulated in order to secure cell proliferation. Previous research has shown that regulation of Mitf is complex and involves regulation of expression, splicing, protein stability and post-translational modifications. Here we show that microRNAs (miRNAs) are also involved in regulating Mitf in melanoma cells. Sequence analysis revealed conserved binding sites for several miRNAs in the Mitf 3'UTR sequence. Furthermore, miR-148 was shown to affect Mitf mRNA expression in melanoma cells through a conserved binding site in the 3'UTR sequence of mouse and human Mitf. In addition we confirm the previously reported effects of miR-137 on Mitf. Other miRNAs, miR-27a, miR-32 and miR-124 which all have conserved binding sites in the Mitf 3'UTR sequence did not have effects on Mitf. Our data show that miR-148 and miR-137 present an additional level of regulating Mitf expression in melanocytes and melanoma cells. Loss of this regulation, either by mutations or by shortening of the 3'UTR sequence, is therefore a likely factor in melanoma formation and/or progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
MiR-101 inhibits melanoma cell invasion and proliferation by targeting MITF and EZH2.Cancer Lett. 2013 Dec 1;341(2):240-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23962556
-
MicroRNA-183-5p regulates MITF expression in vitiligo skin depigmentation.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2022;41(8):703-723. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2022.2066126. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35442159
-
MicroRNA-340-mediated degradation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor mRNA is inhibited by the coding region determinant-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 2;285(27):20532-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.109298. Epub 2010 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):11859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A110.109298. PMID: 20439467 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MITF: master regulator of melanocyte development and melanoma oncogene.Trends Mol Med. 2006 Sep;12(9):406-14. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2006.07.008. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Trends Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16899407 Review.
-
MITF, the Janus transcription factor of melanoma.Future Oncol. 2013 Feb;9(2):235-44. doi: 10.2217/fon.12.177. Future Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23414473 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling Tumour Microenvironment in Melanoma at Single-Cell Level and Challenges to Checkpoint Immunotherapy.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;13(10):1757. doi: 10.3390/genes13101757. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation in human melanoma: past and future.Epigenetics. 2015;10(2):103-21. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2014.1003746. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25587943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The comprehensive detection of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in regulation of mouse melanocyte and skin development.Biol Res. 2020 Feb 3;53(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-0272-1. Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 32014065 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA signatures differentiate melanoma subtypes.Cell Cycle. 2011 Jun 1;10(11):1845-52. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.11.15777. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21543894 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM channels: same ballpark, different players, and different rules in immunogenetics.Immunogenetics. 2011 Dec;63(12):773-87. doi: 10.1007/s00251-011-0570-4. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Immunogenetics. 2011. PMID: 21932052 Review.
References
-
- Steingrimsson E, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. Melanocytes and the microphthalmia transcription factor network. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:365–411. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura EK, Granter SR, Fisher DE. Mechanisms of hair graying: incomplete melanocyte stem cell maintenance in the niche. Science. 2005;307:720–724. - PubMed
-
- Hodgkinson CA, Moore KJ, Nakayama A, Steingrimsson E, Copeland NG, et al. Mutations at the mouse microphthalmia locus are associated with defects in a gene encoding a novel basic-helix-loop-helix-zipper protein. Cell. 1993;74:395–404. - PubMed
-
- Hughes MJ, Lingrel JB, Krakowsky JM, Anderson KP. A helix-loop-helix transcription factor-like gene is located at the mi locus. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:20687–20690. - PubMed
-
- Hemesath TJ, Steingrimsson E, McGill G, Hansen MJ, Vaught J, et al. microphthalmia, a critical factor in melanocyte development, defines a discrete transcription factor family. Genes Dev. 1994;8:2770–2780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

