Novel antibodies reveal inclusions containing non-native SOD1 in sporadic ALS patients
- PMID: 20644736
- PMCID: PMC2904380
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011552
Novel antibodies reveal inclusions containing non-native SOD1 in sporadic ALS patients
Abstract
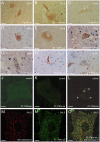
Mutations in CuZn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and are found in 6% of ALS patients. Non-native and aggregation-prone forms of mutant SOD1s are thought to trigger the disease. Two sets of novel antibodies, raised in rabbits and chicken, against peptides spaced along the human SOD1 sequence, were by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and an immunocapture method shown to be specific for denatured SOD1. These were used to examine SOD1 in spinal cords of ALS patients lacking mutations in the enzyme. Small granular SOD1-immunoreactive inclusions were found in spinal motoneurons of all 37 sporadic and familial ALS patients studied, but only sparsely in 3 of 28 neurodegenerative and 2 of 19 non-neurological control patients. The granular inclusions were by confocal microscopy found to partly colocalize with markers for lysosomes but not with inclusions containing TAR DNA binding protein-43, ubiquitin or markers for endoplasmic reticulum, autophagosomes or mitochondria. Granular inclusions were also found in carriers of SOD1 mutations and in spinobulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) patients and they were the major type of inclusion detected in ALS patients homozygous for the wild type-like D90A mutation. The findings suggest that SOD1 may be involved in ALS pathogenesis in patients lacking mutations in the enzyme.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
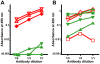
 , denatured SOD1 = “) and 131–153Ra-ab (native SOD1 = ▾, denatured SOD1 = ▿) anti-SOD1 peptide antibodies. The highest concentrations were 0.1 µg/ml, 0.03 µg/ml, 0.1 µg/ml, respectively. (B) Reactivity of antibodies raised to whole SOD1: Rabbit-1 antibody (native SOD1 =
, denatured SOD1 = “) and 131–153Ra-ab (native SOD1 = ▾, denatured SOD1 = ▿) anti-SOD1 peptide antibodies. The highest concentrations were 0.1 µg/ml, 0.03 µg/ml, 0.1 µg/ml, respectively. (B) Reactivity of antibodies raised to whole SOD1: Rabbit-1 antibody (native SOD1 =  ;, denatured SOD1 = “); a sheep antibody from Calbiochem (native = ▴, denatured = ▵); a sheep antibody from The Binding Site (native SOD1 = ▾, denatured SOD1 = ▿); and a mouse monoclonal antibody from Sigma (native SOD1 = ▪, denatured SOD1 =
;, denatured SOD1 = “); a sheep antibody from Calbiochem (native = ▴, denatured = ▵); a sheep antibody from The Binding Site (native SOD1 = ▾, denatured SOD1 = ▿); and a mouse monoclonal antibody from Sigma (native SOD1 = ▪, denatured SOD1 =  ). The highest concentrations were 0.6, 10, 20, and 10 µg/ml, respectively. The data presented are means of 4 wells for each point.
). The highest concentrations were 0.6, 10, 20, and 10 µg/ml, respectively. The data presented are means of 4 wells for each point.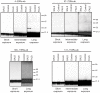
References
-
- Haverkamp LJ, Appel V, Appel SH. Natural history of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a database population. Validation of a scoring system and a model for survival prediction. Brain. 1995;118 (Pt3):707–719. - PubMed
-
- Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Figlewicz DA, Sapp P, et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature. 1993;362:59–62. - PubMed
-
- Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY, et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994;264:1772–1775. - PubMed
-
- Andersen PM, Nilsson P, Ala-Hurula V, Keranen ML, Tarvainen I, et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with homozygosity for an Asp90Ala mutation in CuZn-superoxide dismutase. Nat Genet. 1995;10:61–66. - PubMed
-
- Reaume AG, Elliott JL, Hoffman EK, Kowall NW, Ferrante RJ, et al. Motor neurons in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase-deficient mice develop normally but exhibit enhanced cell death after axonal injury. Nat Genet. 1996;13:43–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

