Effects of DBS on auditory and somatosensory processing in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20645306
- PMCID: PMC6870287
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21096
Effects of DBS on auditory and somatosensory processing in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
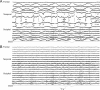
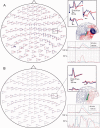
Motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD) can be relieved by deep brain stimulation (DBS). The mechanism of action of DBS is largely unclear. Magnetoencephalography (MEG) studies on DBS patients have been unfeasible because of strong magnetic artifacts. An artifact suppression method known as spatiotemporal signal space separation (tSSS) has mainly overcome these difficulties. We wanted to clarify whether tSSS enables noninvasive measurement of the modulation of cortical activity caused by DBS. We have studied auditory and somatosensory-evoked fields (AEFs and SEFs) of advanced PD patients with bilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN) DBS using MEG. AEFs were elicited by 1-kHz tones and SEFs by electrical pulses to the median nerve with DBS on and off. Data could be successfully acquired and analyzed from 12 out of 16 measured patients. The motor symptoms were significantly relieved by DBS, which clearly enhanced the ipsilateral auditory N100m responses in the right hemisphere. Contralateral N100m responses and somatosensory P60m responses also had a tendency to increase when bilateral DBS was on. MEG with tSSS offers a novel and powerful tool to investigate DBS modulation of the evoked cortical activity in PD with high temporal and spatial resolution. The results suggest that STN-DBS modulates auditory processing in advanced PD. Hum Brain Mapp, 2011. © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Deuschl G, Schade‐Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schafer H, Botzel K, Daniels C, Deutschlander A, Dillmann U, Eisner W, Gruber D, Hamel W, Herzog J, Hilker R, Klebe S, Kloss M, Koy J, Krause M, Kupsch A, Lorenz D, Lorenzl S, Mehdorn HM, Moringlane JR, Oertel W, Pinsker MO, Reichmann H, Reuss A, Schneider GH, Schnitzler A, Steude U, Sturm V, Timmermann L, Tronnier V, Trottenberg T, Wojtecki L, Wolf E, Poewe W, Voges J; German Parkinson Study Group, Neurostimulation Section ( 2006): A randomized trial of deep‐brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 355: 896–908. - PubMed
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR ( 1975): Mini‐mental state: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12: 189–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

