Increased programmed death-ligand-1 expression in human gastric epithelial cells in Helicobacter pylori infection
- PMID: 20646001
- PMCID: PMC2962974
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04217.x
Increased programmed death-ligand-1 expression in human gastric epithelial cells in Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
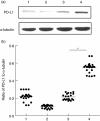
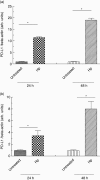
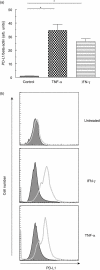
B7-H1 [programmed death-ligand-1 (PD-L1)] is a B7-family member that binds to programmed death-1 (PD-1). Recently, deficiency of PD-L1 has been demonstrated to result in accelerated gastric epithelial cell damage in gastritis, and PD-L1 is suggested to play a critical role in regulating T cell homeostasis. Here, we aimed to gain more insight into gastric PD-L1 expression, regulation and function during Helicobacter pylori infection. PD-L1 expression in human gastric epithelial cells was analysed using Western blotting, quantitative polymerase chain reaction and fluorescence activated cell sorter analysis. Furthermore, co-culture experiments of human gastric epithelial cells with primary human T cells or Jurkat T cells were conducted. PD-L1 expression in primary human gastric epithelial cells was strongly enhanced by H. pylori infection and activated T cells, and augmented markedly by further stimulation with interferon-γ or tumour necrosis factor-α. Moreover, PD-L1 expression in gastric epithelial cells significantly induced apoptosis of T cells. Our results indicate that a novel bidirectional interaction between human gastric epithelial cells and lymphocytes modulates PD-L1 expression in human gastric epithelial cells, contributing to the unique immunological properties of the stomach.
© 2010 British Society for Immunology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PD-L1 is induced in hepatocytes by viral infection and by interferon-alpha and -gamma and mediates T cell apoptosis.J Hepatol. 2006 Oct;45(4):520-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2006.05.007. Epub 2006 Jun 16. J Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16876901
-
Programmed Death Ligand 1-Expressing Classical Dendritic Cells MitigateHelicobacter-Induced Gastritis.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12(2):715-739. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.04.007. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33894424 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of CMTM6 on PD-L1 in Helicobacter pylori infected gastric epithelial cells].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Apr 18;57(2):245-252. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.02.004. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40219552 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Modulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis by Helicobacter pylori in immune pathogenesis of gastric mucosal damage.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017 Feb;50(1):4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2017. PMID: 26947589 Review.
-
Influence of Helicobacter pylori infection on PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy needs more attention.Helicobacter. 2022 Apr;27(2):e12878. doi: 10.1111/hel.12878. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Helicobacter. 2022. PMID: 35112435 Review.
Cited by
-
CD73's Potential as an Immunotherapy Target in Gastrointestinal Cancers.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 15;11:508. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00508. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32351498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter Pylori Promote B7-H1 Expression by Suppressing miR-152 and miR-200b in Gastric Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 5;12(1):e0168822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168822. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28056089 Free PMC article.
-
Delicate Role of PD-L1/PD-1 Axis in Blood Vessel Inflammatory Diseases: Current Insight and Future Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 31;21(21):8159. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218159. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33142805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of The Tumor Microbiome in Tumor Development and Its Treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 15;13:935846. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.935846. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Programmed Death-Ligand 1 is an Early Epithelial Cell Response to Helicobacter pylori Infection.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jan 31;15(1):e1007468. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007468. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30703170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parsonnet J. Molecular mechanisms for inflammation-promoted pathogenesis of cancer – the Sixteenth International Symposium of the Sapporo Cancer Seminar. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3620–4. - PubMed
-
- Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1127–31. - PubMed
-
- Bamford KB, Fan X, Crowe SE, et al. Lymphocytes in the human gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori have a T helper cell 1 phenotype. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:482–92. - PubMed
-
- D'Elios MM, Manghetti M, De Carli M, et al. T helper 1 effector cells specific for Helicobacter pylori in the gastric antrum of patients with peptic ulcer disease. J Immunol. 1997;158:962–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

