Signaling kinase AMPK activates stress-promoted transcription via histone H2B phosphorylation
- PMID: 20647423
- PMCID: PMC3922052
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1191241
Signaling kinase AMPK activates stress-promoted transcription via histone H2B phosphorylation
Abstract
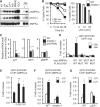
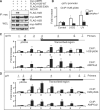
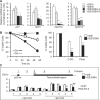
The mammalian adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a serine-threonine kinase protein complex that is a central regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. However, the mechanisms by which AMPK mediates cellular responses to metabolic stress remain unclear. We found that AMPK activates transcription through direct association with chromatin and phosphorylation of histone H2B at serine 36. AMPK recruitment and H2B Ser36 phosphorylation colocalized within genes activated by AMPK-dependent pathways, both in promoters and in transcribed regions. Ectopic expression of H2B in which Ser36 was substituted by alanine reduced transcription and RNA polymerase II association to AMPK-dependent genes, and lowered cell survival in response to stress. Our results place AMPK-dependent H2B Ser36 phosphorylation in a direct transcriptional and chromatin regulatory pathway leading to cellular adaptation to stress.
Figures

Comment in
-
Transcription. Targeting the core of transcription.Science. 2010 Sep 3;329(5996):1158-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1195447. Science. 2010. PMID: 20813944 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

