Recovery and purification process development for monoclonal antibody production
- PMID: 20647768
- PMCID: PMC2958570
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.2.5.12645
Recovery and purification process development for monoclonal antibody production
Abstract
Hundreds of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are currently in development, and many companies have multiple antibodies in their pipelines. Current methodology used in recovery processes for these molecules are reviewed here. Basic unit operations such as harvest, Protein A affinity chromatography, and additional polishing steps are surveyed. Alternative processes such as flocculation, precipitation, and membrane chromatography are discussed. We also cover platform approaches to purification methods development, use of high throughput screening methods, and offer a view on future developments in purification methodology as applied to mAbs.
Figures

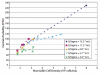



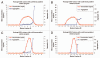



References
-
- Reichert JM, Valge-Archer VE. Development trends for monoclonal antibody cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Fahrner RL, Knudsen HL, Basey CD, Galan W, Feuerhelm D, Vanderlaan M, et al. Industrial purification of pharmaceutical antibodies: development, operation and validation of chromatography processes. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2001;18:301–327. - PubMed
-
- Birch JR, Racher JR. Antibody production. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2006;58:671–685. - PubMed
-
- Kempken R, Pressman A, Berthold W. Assessment of a disc stack centrifuge for use in mammalian cell separation. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1995;46:132–138. - PubMed
-
- Pham C, Lee M, Westoby M, Thommes J. Solid-liquid separation of mammalian cell culture suspensions using a continuous disk stack centrifuge; 3rd International IBC Recovery and Purification Conference; 2002; San Diego, CA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
