Quantum dot-based theranostics
- PMID: 20648364
- PMCID: PMC2965651
- DOI: 10.1039/b9nr00178f
Quantum dot-based theranostics
Abstract
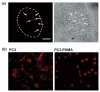
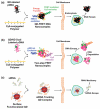
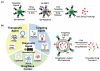
Luminescent semiconductor nanocrystals, also known as quantum dots (QDs), have advanced the fields of molecular diagnostics and nanotherapeutics. Much of the initial progress for QDs in biology and medicine has focused on developing new biosensing formats to push the limit of detection sensitivity. Nevertheless, QDs can be more than passive bio-probes or labels for biological imaging and cellular studies. The high surface-to-volume ratio of QDs enables the construction of a "smart" multifunctional nanoplatform, where the QDs serve not only as an imaging agent but also a nanoscaffold catering for therapeutic and diagnostic (theranostic) modalities. This mini review highlights the emerging applications of functionalized QDs as fluorescence contrast agents for imaging or as nanoscale vehicles for delivery of therapeutics, with special attention paid to the promise and challenges towards QD-based theranostics.
Figures
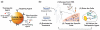

Similar articles
-
Multifunctional quantum dots-based cancer diagnostics and stem cell therapeutics for regenerative medicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Dec 1;95:2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 26344675 Review.
-
Design of multifunctional liposome-quantum dot hybrid nanocarriers and their biomedical application.J Drug Target. 2017 Sep;25(8):661-672. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2017.1323334. Epub 2017 May 8. J Drug Target. 2017. PMID: 28438041 Review.
-
Highly-sensitive aptasensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between l-cysteine capped ZnS quantum dots and graphene oxide sheets for the determination of edifenphos fungicide.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Oct 15;96:324-331. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.05.028. Epub 2017 May 12. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28525850
-
Quantum Dot-Based Nanotools for Bioimaging, Diagnostics, and Drug Delivery.Chembiochem. 2016 Nov 17;17(22):2103-2114. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201600357. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Chembiochem. 2016. PMID: 27535363 Review.
-
Semiconductor quantum dots as contrast agents for whole animal imaging.Trends Biotechnol. 2004 Dec;22(12):607-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.10.012. Trends Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15542145 Review.
Cited by
-
Introduction of Nanobiotechnology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1309:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-6158-4_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33782866
-
Quantum dot-based nanoprobes for in vivo targeted imaging.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Dec;13(10):1549-67. doi: 10.2174/1566524013666131111121733. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24206136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantum Dots Encapsulated with Canine Parvovirus-Like Particles Improving the Cellular Targeted Labeling.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 23;10(9):e0138883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138883. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26398132 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Receptor Structure and Length on the Wrapping of a Nanoparticle by a Lipid Membrane.Materials (Basel). 2014 May 14;7(5):3855-3866. doi: 10.3390/ma7053855. Materials (Basel). 2014. PMID: 28788653 Free PMC article.
-
Phototheranostics for multifunctional treatment of cancer with fluorescence imaging.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Oct;189:114483. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114483. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35944585 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Niemeyer CM. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:4128–4158. - PubMed
-
- Penn SG, He L, Natan MJ. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003;7:609–615. - PubMed
-
- Katz E, Willner I. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004;43:6042–6108. - PubMed
-
- De M, Ghosh PS, Rotello VM. Adv. Mater. 2008;20:4225–4241.
-
- Nirmal M, Brus L. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999;32:407–414.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

