Temporal weighting of interaural time and level differences in high-rate click trains
- PMID: 20649228
- PMCID: PMC2921433
- DOI: 10.1121/1.3436540
Temporal weighting of interaural time and level differences in high-rate click trains
Abstract
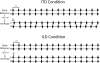
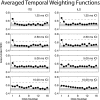
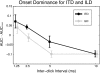
Temporal weighting functions (TWFs), quantifying sensitivity to interaural time differences (ITD) and interaural level differences (ILD) over the duration of brief stimuli, were measured in 6 normal hearing subjects using trains of 16 Gabor clicks centered at 4 kHz presented dichotically at 4 rates [inter-click intervals (ICI) of 10, 5, 2.5, and 1.25 ms]. Random ITD or ILD were imposed independently on each click in the train in separate conditions. The subject's task was to discriminate the lateral position of the click train ("left" or "right"). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was then used to quantify the effectiveness or "weight" of each click according to individual click ITD or ILD. Although individual differences were evident, onset cues appeared to dominate at high rates. Onset dominance was apparent for both ITD and ILD at 1.25 ms ICI and for ITD at 2.5 ms ICI, but for neither cue at 5 or 10 ms ICI. Onset dominance was greater on average for ITD than ILD, although TWFs were qualitatively similar for the two cues. No evidence was found for "upweighting" of late-arriving ILD [Stecker, G. C., and Hafter, E. R. (2009), J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125, 3914-3924].
Figures


References
-
- Blauert, J. (1997). Spatial Hearing: The Psychophysics of Human Sound Localization, revised ed. (MIT, Cambridge, MA: ).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

