Darbepoetin-mediated cardioprotection after myocardial infarction involves multiple mechanisms independent of erythropoietin receptor-common beta-chain heteroreceptor
- PMID: 20649603
- PMCID: PMC2958651
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00876.x
Darbepoetin-mediated cardioprotection after myocardial infarction involves multiple mechanisms independent of erythropoietin receptor-common beta-chain heteroreceptor
Abstract
Background and purpose: Darbepoetin, a long-acting erythropoietin derivative, attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improves short-term (3 days) cardiac function, but the mechanisms responsible are unknown. We investigated potential mechanisms by which darbepoetin exerts cardioprotection following myocardial infarction in mice and the significance of the erythropoietin receptor (EPOR)-common beta-chain (c-beta-chain) heteroreceptor.
Experimental approach: Mice underwent 60 min coronary occlusion followed by treatment with vehicle or a single dose of darbepoetin. Effects on gene expression, apoptosis and neutrophil accumulation in infarcted left ventricle were assessed 24 h later. Cardiac function, effects on vascularization and fibrosis were assessed 28 days later. The significance of EPOR-c-beta-chain heteroreceptor was examined 28 days after infarction using mice deficient in c-beta-chain.
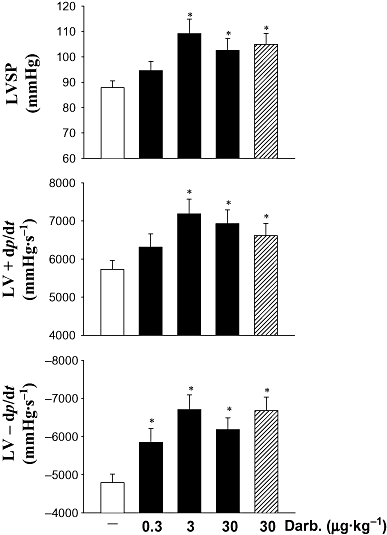
Key results: Twenty-four hours after darbepoetin, mRNAs encoding haeme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), iNOS and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) were markedly elevated only in infarcted regions, and the frequency of apoptotic cells attenuated. Inflammation was also attenuated with reductions in neutrophil numbers. Darbepoetin also elevated mRNAs encoding angiogenic factors: placental growth factor, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin-1beta. Twenty-eight days after treatment, CD31+ vessels in the infarct zone doubled and fibrosis reduced. Cardiac haemodynamics were improved. Darbepoetin also improved cardiac haemodynamics in c-beta-chain-deficient mice, increased HO-1 and iNOS expression and vessel numbers and attenuated fibrosis.
Conclusions and implications: Darbepoetin stimulates expression of haeme oxygenase, iNOS, BNP and angiogenic factors specifically in infarcted left ventricle that attenuates inflammation, apoptosis and fibrosis; elevate vessel numbers; and improve cardiac function. The EPOR-c-beta-chain heteroreceptor is not essential for these effects.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activator protein-2α mediates carbon monoxide-induced stromal cell-derived factor-1α expression and vascularization in ischemic heart.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Apr;33(4):785-94. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301143. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23393395
-
Post-infarct treatment with [Pyr(1)]apelin-13 improves myocardial function by increasing neovascularization and overexpression of angiogenic growth factors in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug 15;761:101-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.04.034. Epub 2015 May 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25936512
-
Erythropoietin attenuates cardiac dysfunction by increasing myocardial angiogenesis and inhibiting interstitial fibrosis in diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012 Sep 7;11:105. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-105. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012. PMID: 22954171 Free PMC article.
-
Exendin-4 induces myocardial protection through MKK3 and Akt-1 in infarcted hearts.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Feb 15;310(4):C270-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00194.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26739490 Free PMC article.
-
Qiliqiangxin improves cardiac function and attenuates cardiac remodeling in rats with experimental myocardial infarction.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6596-606. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261541 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Second-generation non-hematopoietic erythropoietin-derived peptide for neuroprotection.Redox Biol. 2022 Feb;49:102223. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102223. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 34953452 Free PMC article.
-
Improved cerebrovascular function and reduced histological damage with darbepoietin alfa administration after cortical impact injury in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 May;337(2):451-6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.176602. Epub 2011 Jan 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21270134 Free PMC article.
-
EPO does not promote interaction between the erythropoietin and beta-common receptors.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 20;8(1):12457. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29865-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30127368 Free PMC article.
-
Non-erythroid effects of erythropoietin.Haematologica. 2010 Nov;95(11):1803-5. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.030213. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 21037325 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
EPOR2/βcR2-independendent effects of low-dose epoetin-α in porcine liver transplantation.Biosci Rep. 2017 Dec 5;37(6):BSR20171007. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171007. Print 2017 Dec 22. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29127105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker JE, Kozik D, Hsu AK, Fu X, Tweddell JS, Gross GJ. Darbepoetin alfa protects the rat heart against infarction: dose–response, phase of action, and mechanisms. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;49:337–345. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Zhao W, Vigdorchik A, Belayev A, Busto R, et al. Neuroprotective effect of darbepoetin alfa, a novel recombinant erythropoietic protein, in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2005;36:1071–1076. - PubMed
-
- Brouard S, Berberat PO, Tobiasch E, Seldon MP, Bach FH, Soares MP. Heme oxygenase-1-derived carbon monoxide requires the activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B to protect endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:17950–17961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

