The effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on obesity in postmenopausal women: secondary analysis for a large-scale, placebo controlled, double-blind, 4-year longitudinal clinical trial
- PMID: 20650013
- PMCID: PMC3161354
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-62
The effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on obesity in postmenopausal women: secondary analysis for a large-scale, placebo controlled, double-blind, 4-year longitudinal clinical trial
Abstract
Background: It is undetermined whether calcium supplementation has an effect on obesity or body composition in postmenopausal women. The purpose of the study is to detect the effect of calcium supplementation on indices of obesity and body composition.
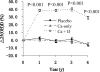
Methods: This is a secondary analysis of data from a population-based, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial designed to determine the effects of calcium and vitamin D on osteoporotic fractures. The cohort included 1179 postmenopausal women who were randomly assigned into one of three groups: 1) supplemental calcium (1400 mg/d or 1500 mg/d) plus vitamin D placebo (Ca-only group); 2) supplemental calcium (1400 mg/d or 1500 mg/d) plus supplemental vitamin D3 (1100 IU/d) (Ca + D group); or, 3) two placebos (placebo group). After applying the exclusion criteria for this analysis, 870 subjects were included in this study. The primary outcomes for the present study were changes in body mass index, trunk fat, trunk lean, and percentage of trunk fat after calcium supplementation.
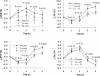
Results: Changes in trunk fat, trunk lean, and percentage of trunk fat were significantly different between the calcium intervention groups (Ca-only group or Ca + D group) and the placebo group during the trial (P < 0.05). The calcium intervention groups gained less trunk fat and maintained more trunk lean when compared to the placebo group. No significant difference was observed for body mass index between groups.
Conclusion: Calcium supplementation over four years has a beneficial effect on body composition in postmenopausal women.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of different amounts of vitamin D supplementation on serum calcidiol, anthropometric status, and body composition in overweight or obese nursing women: a study protocol for a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial.Trials. 2019 Aug 30;20(1):542. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3622-y. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31470899 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Vitamin D and Calcium Supplementation on Cancer Incidence in Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 Mar 28;317(12):1234-1243. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.2115. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28350929 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of isolated vitamin D supplementation on bone turnover markers in younger postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Osteoporos Int. 2018 May;29(5):1125-1133. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4395-y. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29450585 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation alone on muscle function in postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.Osteoporos Int. 2015 Oct;26(10):2413-21. doi: 10.1007/s00198-015-3151-9. Epub 2015 May 9. Osteoporos Int. 2015. PMID: 25956283 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Calcium Plus Vitamin D Supplementation on Anthropometric Measurements and Blood Pressure in Vitamin D Insufficient People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(4):281-9. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2014.905761. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25738212 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effects of calcium-vitamin D co-supplementation on metabolic profiles in vitamin D insufficient people with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled clinical trial.Diabetologia. 2014 Oct;57(10):2038-47. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3313-x. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Diabetologia. 2014. PMID: 25005333 Clinical Trial.
-
A 12-week double-blind randomized clinical trial of vitamin D₃ supplementation on body fat mass in healthy overweight and obese women.Nutr J. 2012 Sep 22;11:78. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-11-78. Nutr J. 2012. PMID: 22998754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, parathyroid hormone and blood pressure in an elderly cohort from Germany: a cross-sectional study.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012 Mar 21;9(1):20. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-20. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22433818 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms affecting changes in visceral fat, waist circumference and lipid profile in breast cancer survivors supplemented with vitamin D3.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Aug 9;18(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1100-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31395070 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Genetic variants of VDR and CYP2R1 affect BMI independently of serum vitamin D concentrations.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Jun 13;21(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-01065-3. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32534577 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

