Update of human and mouse forkhead box (FOX) gene families
- PMID: 20650821
- PMCID: PMC3500164
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-4-5-345
Update of human and mouse forkhead box (FOX) gene families
Abstract
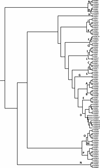
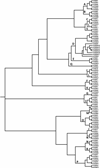
The forkhead box (FOX) proteins are transcription factors that play complex and important roles in processes from development and organogenesis to regulation of metabolism and the immune system. There are 50 FOX genes in the human genome and 44 in the mouse, divided into 19 subfamilies. All human FOX genes have close mouse orthologues, with one exception: the mouse has a single Foxd4 , whereas the human gene has undergone a recent duplication to a total of seven ( FOXD4 and FOXD4L1 --> FOXD4L6 ). Evolutionarily ancient family members can be found as far back as the fungi and metazoans. The DNA-binding domain, the forkhead domain, is an example of the winged-helix domain, and is very well conserved across the FOX family and across species, with a few notable exceptions in which divergence has created new functionality. Mutations in FOX genes have been implicated in at least four familial human diseases, and differential expression may play a role in a number of other pathologies - ranging from metabolic disorders to autoimmunity. Furthermore, FOX genes are differentially expressed in a large number of cancers; their role can be either as an oncogene or tumour suppressor, depending on the family member and cell type. Although some drugs that target FOX gene expression or activity, notably proteasome inhibitors, appear to work well, much more basic research is needed to unlock the complex interplay of upstream and downstream interactions with FOX family transcription factors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

