Identification of phosphomethylethanolamine N-methyltransferase from Arabidopsis and its role in choline and phospholipid metabolism
- PMID: 20650897
- PMCID: PMC2937945
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.112151
Identification of phosphomethylethanolamine N-methyltransferase from Arabidopsis and its role in choline and phospholipid metabolism
Abstract
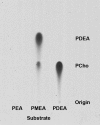
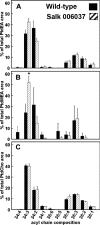
Three sequential methylations of phosphoethanolamine (PEA) are required for the synthesis of phosphocholine (PCho) in plants. A cDNA encoding an N-methyltransferase that catalyzes the last two methylation steps was cloned from Arabidopsis by heterologous complementation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae cho2, opi3 mutant. The cDNA encodes phosphomethylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PMEAMT), a polypeptide of 475 amino acids that is organized as two tandem methyltransferase domains. PMEAMT shows 87% amino acid identity to a related enzyme, phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase, an enzyme in plants that catalyzes all three methylations of PEA to PCho. PMEAMT cannot use PEA as a substrate, but assays using phosphomethylethanolamine as a substrate result in both phosphodimethylethanolamine and PCho as products. PMEAMT is inhibited by the reaction products PCho and S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine, a property reported for phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase from various plants. An Arabidopsis mutant with a T-DNA insertion associated with locus At1g48600 showed no transcripts encoding PMEAMT. Shotgun lipidomic analyses of leaves of atpmeamt and wild-type plants generated phospholipid profiles showing the content of phosphatidylmethylethanolamine to be altered relative to wild type with the content of a 34:3 lipid molecular species 2-fold higher in mutant plants. In S. cerevisiae, an increase in PtdMEA in membranes is associated with reduced viability. This raises a question regarding the role of PMEAMT in plants and whether it serves to prevent the accumulation of PtdMEA to potentially deleterious levels.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The isolation and characterization in yeast of a gene for Arabidopsis S-adenosylmethionine:phospho-ethanolamine N-methyltransferase.Plant Physiol. 2000 Dec;124(4):1800-13. doi: 10.1104/pp.124.4.1800. Plant Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11115895 Free PMC article.
-
The xipotl mutant of Arabidopsis reveals a critical role for phospholipid metabolism in root system development and epidermal cell integrity.Plant Cell. 2004 Aug;16(8):2020-34. doi: 10.1105/tpc.103.018648. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15295103 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of phospholipid N-methyltransferases from Arabidopsis and soybean.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jun 5;284(23):15439-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.005991. Epub 2009 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19366698 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological roles of phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar;1831(3):626-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.07.017. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22877991 Review.
-
Metabolic crosstalk between choline/1-carbon metabolism and energy homeostasis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013 Mar 1;51(3):467-75. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0518. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23072856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pi starvation-dependent regulation of ethanolamine metabolism by phosphoethanolamine phosphatase PECP1 in Arabidopsis roots.J Exp Bot. 2018 Jan 23;69(3):467-481. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx408. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 29294054 Free PMC article.
-
Covering their bases: The phosphobase methylation pathway in plants.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21703-21704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H117.000712. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29288241 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid biosynthesis and protein concentration respond uniquely to phosphate supply during leaf development in highly phosphorus-efficient Hakea prostrata.Plant Physiol. 2014 Dec;166(4):1891-911. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.248930. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25315604 Free PMC article.
-
A Methyltransferase Trio Essential for Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis and Growth.Plant Physiol. 2019 Feb;179(2):433-445. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01408. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30518673 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and Functional Analysis of Phosphoethanolamine Methyltransferase Promoter from Maize (Zea mays L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 8;19(1):191. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010191. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29316727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang J., Rozwadowski K., Bhinu V. S., Schäfer U., Hannoufa A. (2008) Plant Physiol. Biochem. 46, 647–654 - PubMed
-
- Zeisel S. H., Da Costa K. A., Franklin P. D., Alexander E. A., Lamont J. T., Sheard N. F., Beiser A. (1991) FASEB J. 5, 2093–2098 - PubMed
-
- Blusztajn J. K. (1998) Science 281, 794–795 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

