Identification of direct and indirect effectors of the transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) cation channel
- PMID: 20650899
- PMCID: PMC2943302
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066464
Identification of direct and indirect effectors of the transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) cation channel
Abstract
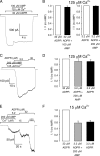
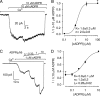
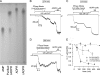
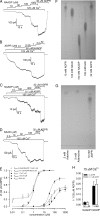
Transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) is a Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel involved in physiological and pathophysiological processes linked to oxidative stress. TRPM2 channels are co-activated by intracellular Ca(2+) and ADP-ribose (ADPR) but also modulated in intact cells by several additional factors. Superfusion of TRPM2-expressing cells with H(2)O(2) or intracellular dialysis of cyclic ADPR (cADPR) or nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) activates, whereas dialysis of AMP inhibits, TRPM2 whole-cell currents. Additionally, H(2)O(2), cADPR, and NAADP enhance ADPR sensitivity of TRPM2 currents in intact cells. Because in whole-cell recordings the entire cellular machinery for nucleotide and Ca(2+) homeostasis is intact, modulators might affect TRPM2 activity either directly, by binding to TRPM2, or indirectly, by altering the local concentrations of the primary ligands ADPR and Ca(2+). To identify direct modulators of TRPM2, we have studied the effects of H(2)O(2), AMP, cADPR, NAADP, and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide in inside-out patches from Xenopus oocytes expressing human TRPM2, by directly exposing the cytosolic faces of the patches to these compounds. H(2)O(2) (1 mM) and enzymatically purified cADPR (10 μM) failed to activate, whereas AMP (200 μM) failed to inhibit TRPM2 currents. NAADP was a partial agonist (maximal efficacy, ∼50%), and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide was a full agonist, but both had very low affinities (K(0.5) = 104 and 35 μM). H(2)O(2), cADPR, and NAADP did not enhance activation by ADPR. Considering intracellular concentrations of these compounds, none of them are likely to directly affect the TRPM2 channel protein in a physiological context.
Figures



References
-
- Nagamine K., Kudoh J., Minoshima S., Kawasaki K., Asakawa S., Ito F., Shimizu N. (1998) Genomics 54, 124–131 - PubMed
-
- Perraud A. L., Fleig A., Dunn C. A., Bagley L. A., Launay P., Schmitz C., Stokes A. J., Zhu Q., Bessman M. J., Penner R., Kinet J. P., Scharenberg A. M. (2001) Nature 411, 595–599 - PubMed
-
- Sano Y., Inamura K., Miyake A., Mochizuki S., Yokoi H., Matsushime H., Furuichi K. (2001) Science 293, 1327–1330 - PubMed
-
- Hara Y., Wakamori M., Ishii M., Maeno E., Nishida M., Yoshida T., Yamada H., Shimizu S., Mori E., Kudoh J., Shimizu N., Kurose H., Okada Y., Imoto K., Mori Y. (2002) Mol. Cell 9, 163–173 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

