Ileal apical Na+-dependent bile acid transporter ASBT is upregulated in rats with diabetes mellitus induced by low doses of streptozotocin
- PMID: 20651004
- PMCID: PMC2957331
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00139.2010
Ileal apical Na+-dependent bile acid transporter ASBT is upregulated in rats with diabetes mellitus induced by low doses of streptozotocin
Abstract
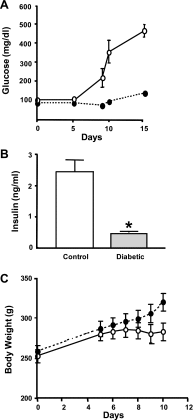
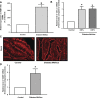
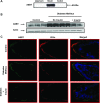
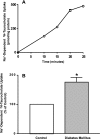
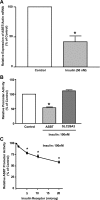
Increased intestinal bile acid absorption and expansion of the bile acid pool has been implicated in the hypercholesterolemia associated with diabetes mellitus. However, the molecular basis of the increase in bile acid absorption in diabetes mellitus is not fully understood. The ileal apical Na(+)-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) is primarily responsible for active reabsorption of the majority of bile acids. Current studies were designed to investigate the modulation of ASBT function and expression in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes mellitus in rats and to examine the effect of insulin on rat ASBT promoter by insulin. Diabetes mellitus was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats by intraperitoneal injection of low doses of STZ (20 mg/kg body wt) on five consecutive days. Human insulin (10 U/day) was given to a group of diabetic rats for 3 days before euthanasia. RNA and protein were extracted from mucosa isolated from the small intestine and ASBT expression was assessed by real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Western blotting. Our data showed that ASBT mRNA and protein expression were significantly elevated in diabetic rats. Insulin treatment of diabetic rats reversed the increase in ASBT protein expression to control levels. Consistently, ileal Na(+)-dependent [(3)H]taurocholic uptake in isolated intestinal epithelial cells was significantly increased in diabetic rats. In vitro studies utilizing intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells demonstrated that ASBT expression and promoter activity were significantly decreased by insulin. These studies demonstrated that insulin directly influences ASBT expression and promoter activity and that ASBT function and expression are increased in rats with STZ-induced diabetes mellitus. The increase in ASBT expression may contribute to disturbances in cholesterol homeostasis associated with diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Alrefai WA, Gill RK. Bile acid transporters: structure, function, regulation and pathophysiological omplications. Pharm Res 24: 1803–1823, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bennion LJ, Grundy SM. Effects of diabetes mellitus on cholesterol metabolism in man. N Engl J Med 296: 1365–1371, 1977. - PubMed
-
- Bhat BG, Rapp SR, Beaudry JA, Napawan N, Butteiger DN, Hall KA, Null CL, Luo Y, Keller BT. Inhibition of ileal bile acid transport and reduced atherosclerosis in apoE-/- mice by SC-435. J Lipid Res 44: 1614–1621, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254, 1976. - PubMed
-
- Brenna O, Qvigstad G, Brenna E, Waldum HL. Cytotoxicity of streptozotocin on neuroendocrine cells of the pancreas and the gut. Dig Dis Sci 48: 906–910, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

