Chronic ethanol consumption enhances sensitivity to Ca(2+)-mediated opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and increases cyclophilin D in liver
- PMID: 20651005
- PMCID: PMC2957342
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00246.2010
Chronic ethanol consumption enhances sensitivity to Ca(2+)-mediated opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and increases cyclophilin D in liver
Abstract
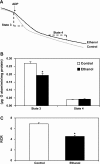
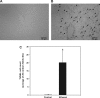
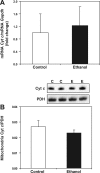
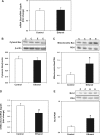
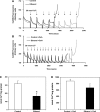
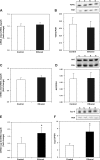
Chronic ethanol consumption increases mitochondrial oxidative stress and sensitivity to form the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP). The mechanism responsible for increased MPTP sensitivity in ethanol-exposed mitochondria and its relation to mitochondrial Ca(2+) handling is unknown. Herein, we investigated whether increased sensitivity to MPTP induction in liver mitochondria from ethanol-fed rats compared with controls is related to an ethanol-dependent change in mitochondrial Ca(2+) accumulation. Liver mitochondria were isolated from control and ethanol-fed rats, and Ca(2+)-mediated induction of the MPTP and mitochondrial Ca(2+) retention capacity were measured. Levels of proposed MPTP proteins as well as select pro- and antiapoptotic proteins were measured along with gene expression. We observed increased steatosis and TUNEL-stained nuclei in liver of ethanol-fed rats compared with controls. Liver mitochondria from ethanol-fed rats had increased levels of proapoptotic Bax protein and reduced Ca(2+) retention capacity compared with control mitochondria. We observed increased cyclophilin D (Cyp D) gene expression in liver and protein in mitochondria from ethanol-fed animals compared with controls, whereas there was no change in the adenine nucleotide translocase and voltage-dependent anion channel. Together, these results suggest that enhanced sensitivity to Ca(2+)-mediated MPTP induction may be due, in part, to higher Cyp D levels in liver mitochondria from ethanol-fed rats. Therefore, therapeutic strategies aimed at normalizing Cyp D levels may be beneficial in preventing ethanol-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction and liver injury.
Figures


References
-
- Adachi M, Higuchi H, Miura S, Azuma T, Inokuchi S, Saito H, Kato S, Ishii H. Bax interacts with the voltage-dependent anion channel and mediates ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287: G695–G705, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Albano E. Alcohol, oxidative stress and free radical damage. Proc Nutr Soc 65: 278–290, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Andringa KK, King AL, Eccleston HB, Mantena SK, Landar A, Jhala NC, Dickinson DA, Squadrito GL, Bailey SM. Analysis of the liver mitochondrial proteome in response to ethanol and S-adenosylmethionine treatments: novel molecular targets of disease and hepatoprotection. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298: G732–G745, 2010. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonsson B. Bax and other pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family “killer-proteins” and their victim the mitochondrion. Cell Tissue Res 306: 347–361, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

