Identification of a microRNA signature of renal ischemia reperfusion injury
- PMID: 20651252
- PMCID: PMC2922548
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912701107
Identification of a microRNA signature of renal ischemia reperfusion injury
Abstract
Renal ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Given the importance of microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating gene expression, we examined expression profiles of miRNAs following renal IRI. Global miRNA expression profiling on samples prepared from the kidneys of C57BL/6 mice that underwent unilateral warm ischemia revealed nine miRNAs (miR-21, miR-20a, miR-146a, miR-199a-3p, miR-214, miR-192, miR-187, miR-805, and miR-194) that are differentially expressed following IRI when compared with sham controls. These miRNAs were also differently expressed following IRI in immunodeficient RAG-2/common gamma-chain double-knockout mice, suggesting that the changes in expression observed are not significantly influenced by lymphocyte infiltration and therefore define a lymphocyte-independent signature of renal IRI. In vitro studies revealed that miR-21 is expressed in proliferating tubular epithelial cells (TEC) and up-regulated by both cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic mechanisms resulting from ischemia and TGF-beta signaling, respectively. In vitro, knockdown of miR-21 in TEC resulted in increased cell death, whereas overexpression prevented cell death. However, overexpression of miR-21 alone was not sufficient to prevent TEC death following ischemia. Our findings therefore define a molecular fingerprint of renal injury and suggest miR-21 may play a role in protecting TEC from death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

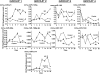

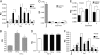
References
-
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1448–1460. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3365–3370. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV, Zuk A. Ischemic acute renal failure: An inflammatory disease? Kidney Int. 2004;66:480–485. - PubMed
-
- Jang HR, Ko GJ, Wasowska BA, Rabb H. The interaction between ischemia-reperfusion and immune responses in the kidney. J Mol Med. 2009;87:859–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

