Alkali production associated with malolactic fermentation by oral streptococci and protection against acid, oxidative, or starvation damage
- PMID: 20651853
- PMCID: PMC3070543
- DOI: 10.1139/w10-039
Alkali production associated with malolactic fermentation by oral streptococci and protection against acid, oxidative, or starvation damage
Abstract
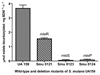
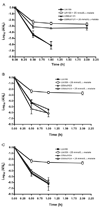
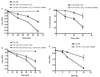
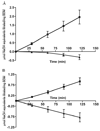
Alkali production by oral streptococci is considered important for dental plaque ecology and caries moderation. Recently, malolactic fermentation (MLF) was identified as a major system for alkali production by oral streptococci, including Streptococcus mutans. Our major objectives in the work described in this paper were to further define the physiology and genetics of MLF of oral streptococci and its roles in protection against metabolic stress damage. L-Malic acid was rapidly fermented to L-lactic acid and CO(2) by induced cells of wild-type S. mutans, but not by deletion mutants for mleS (malolactic enzyme) or mleP (malate permease). Mutants for mleR (the contiguous regulator gene) had intermediate capacities for MLF. Loss of capacity to catalyze MLF resulted in loss of capacity for protection against lethal acidification. MLF was also found to be protective against oxidative and starvation damage. The capacity of S. mutans to produce alkali from malate was greater than its capacity to produce acid from glycolysis at low pH values of 4 or 5. MLF acted additively with the arginine deiminase system for alkali production by Streptococcus sanguinis, but not with urease of Streptococcus salivarius. Malolactic fermentation is clearly a major process for alkali generation by oral streptococci and for protection against environmental stresses.
Figures



References
-
- Acevedo AM, Montero M, Rojas-Sanchez F, Machado C, Rivera LE, Wolff M, Kleinberg I. Clinical evaluation of the ability of CaviStat in a mint confection to inhibit the development of dental caries in children. J. Clin. Dent. 2008;19(1):1–8. PMID:18500152. - PubMed
-
- Ansanay V, Dequin S, Blondin B, Barre P. Cloning, sequence and expression of the gene encoding the malolactic enzyme from Lactococcus lactis. FEBS Lett. 1993;332(1–2):74–80. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(93)80488-G. PMID:8405453. - PubMed
-
- Baldeck JD, Marquis RE. Targets for hydrogen-peroxide-induced damage to suspension and biofilm cells of Streptococcus mutans. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008;54(10):868–875. doi:10.1139/W08-078. PMID:18923556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

