Inhibition of melanoma angiogenesis by telomere homolog oligonucleotides
- PMID: 20652008
- PMCID: PMC2906154
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/928628
Inhibition of melanoma angiogenesis by telomere homolog oligonucleotides
Abstract
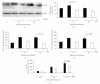
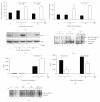
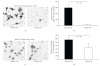
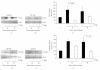
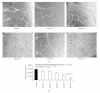
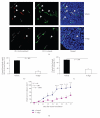
Telomere homolog oligonucleotides (T-oligos) activate an innate telomere-based program that leads to multiple anticancer effects. T-oligos act at telomeres to initiate signaling through the Werner protein and ATM kinase. We wanted to determine if T-oligos have antiangiogenic effects. We found that T-oligo-treated human melanoma (MM-AN) cells had decreased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptor 2, angiopoeitin-1 and -2 and decreased VEGF secretion. T-oligos activated the transcription factor E2F1 and inhibited the activity of the angiogenic transcription factor, HIF-1alpha. T-oligos inhibited EC tubulogenesis and total tumor microvascular density matrix invasion by MM-AN cells and ECs in vitro. In melanoma SCID xenografts, two systemic T-oligo injections decreased by 60% (P < .004) total tumor microvascular density and the functional vessels density by 80% (P < .002). These findings suggest that restriction of tumor angiogenesis is among the host's innate telomere-based anticancer responses and provide further evidence that T-oligos may offer a powerful new approach for melanoma treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treating Cancer by Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase.Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Feb 19;6(1):15. doi: 10.3390/antiox6010015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28218725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligonucleotides Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase in Cancer.Molecules. 2018 Sep 5;23(9):2267. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092267. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30189661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere-based DNA damage responses: a new approach to melanoma.FASEB J. 2004 Sep;18(12):1373-81. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1774com. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15333580
-
Novel delivery system for T-oligo using a nanocomplex formed with an alpha helical peptide for melanoma therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:43-53. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S55133. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24391441 Free PMC article.
-
Telomeric DNA induces apoptosis and senescence of human breast carcinoma cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(1):R13. doi: 10.1186/bcr1646. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17257427 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Beyond Telomerase: Telomere Instability as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy.J Mol Genet Med. 2013 Dec;7(4):91. doi: 10.4172/1747-0862.1000091. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Mol Genet Med. 2013. PMID: 27123041 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase in Cancer: Function, Regulation, and Clinical Translation.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 5;14(3):808. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030808. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating Cancer by Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase.Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Feb 19;6(1):15. doi: 10.3390/antiox6010015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28218725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligonucleotides Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase in Cancer.Molecules. 2018 Sep 5;23(9):2267. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092267. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30189661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking the 'harmony' of TNF-α signaling for cancer treatment.Oncogene. 2012 Sep 13;31(37):4117-27. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.567. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22158049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis. Annual Review of Medicine. 2006;57:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Chen C-H, Jiang W, Via DP, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoproteins inhibit endothelial cell proliferation by suppressing basic fibroblast growth factor expression. Circulation. 2000;101(2):171–177. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury D, Clarke D, Seedhouse C, Corbettt L, Stocks J, Knox A. Vascular endothelial growth factor induction by prostaglandin E2 in human airway smooth muscle cells is mediated by E prostanoid EP 2/EP4 receptors and SP-1 transcription factor binding sites. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280(34):29993–30000. - PubMed
-
- Pagès G, Pouysségur J. Transcriptional regulation of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor gene—a concert of activating factors. Cardiovascular Research. 2005;65(3):564–573. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

