Adipocytokines in atherothrombosis: focus on platelets and vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 20652043
- PMCID: PMC2905911
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/174341
Adipocytokines in atherothrombosis: focus on platelets and vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
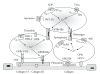
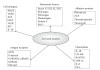
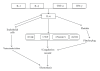
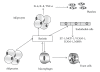
Visceral obesity is a relevant pathological condition closely associated with high risk of atherosclerotic vascular disease including myocardial infarction and stroke. The increased vascular risk is related also to peculiar dysfunction in the endocrine activity of adipose tissue responsible of vascular impairment (including endothelial dysfunction), prothrombotic tendency, and low-grade chronic inflammation. In particular, increased synthesis and release of different cytokines, including interleukins and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and adipokines-such as leptin-have been reported as associated with future cardiovascular events. Since vascular cell dysfunction plays a major role in the atherothrombotic complications in central obesity, this paper aims at focusing, in particular, on the relationship between platelets and vascular smooth muscle cells, and the impaired secretory pattern of adipose tissue.
Figures


References
-
- Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ôunpuu S, et al. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27 000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. The Lancet. 2005;366(9497):1640–1649. - PubMed
-
- Lebovitz HE, Banerji MA. Point: visceral adiposity is causally related to insulin resistance. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(9):2322–2325. - PubMed
-
- Klein S, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, et al. Waist circumference and cardiometabolic risk: a consensus statement from Shaping America’s Health: association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, the Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition; and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(6):1647–1652. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120(16):1640–1645. - PubMed
-
- Reaven G, Abbasi F, McLaughlin T. Obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease. Recent Progress in Hormone Research. 2004;59:207–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

