A Quick and Parallel Analytical Method Based on Quantum Dots Labeling for ToRCH-Related Antibodies
- PMID: 20652102
- PMCID: PMC2894333
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-009-9422-7
A Quick and Parallel Analytical Method Based on Quantum Dots Labeling for ToRCH-Related Antibodies
Abstract
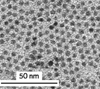
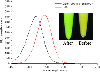
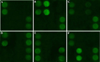
Quantum dot is a special kind of nanomaterial composed of periodic groups of II-VI, III-V or IV-VI materials. Their high quantum yield, broad absorption with narrow photoluminescence spectra and high resistance to photobleaching, make them become a promising labeling substance in biological analysis. Here, we report a quick and parallel analytical method based on quantum dots for ToRCH-related antibodies including Toxoplasma gondii, Rubella virus, Cytomegalovirus and Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV1) and 2 (HSV2). Firstly, we fabricated the microarrays with the five kinds of ToRCH-related antigens and used CdTe quantum dots to label secondary antibody and then analyzed 100 specimens of randomly selected clinical sera from obstetric outpatients. The currently prevalent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were considered as "golden standard" for comparison. The results show that the quantum dots labeling-based ToRCH microarrays have comparable sensitivity and specificity with ELISA. Besides, the microarrays hold distinct advantages over ELISA test format in detection time, cost, operation and signal stability. Validated by the clinical assay, our quantum dots-based ToRCH microarrays have great potential in the detection of ToRCH-related pathogens.
Keywords: Antibody; Diagnosis; Microarray; Quantum dots; Serology.
Figures


References
-
- Inoue H, Matsuyama A, Mimori K, Ueo H, Mori M, Chong JM, Fukayama M, Kodama T, Aburatani H. Clin. 2002. p. 3475. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XpsVCgtLw%3D]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

