Rapid Concentration of Nanoparticles with DC Dielectrophoresis in Focused Electric Fields
- PMID: 20652137
- PMCID: PMC2893963
- DOI: 10.1007/s11671-009-9442-3
Rapid Concentration of Nanoparticles with DC Dielectrophoresis in Focused Electric Fields
Abstract
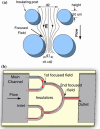
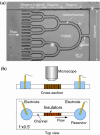
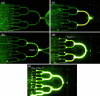
We report a microfluidic device for rapid and efficient concentration of micro/nanoparticles with direct current dielectrophoresis (DC DEP). The concentrator is composed of a series of microchannels constructed with PDMS-insulating microstructures for efficiently focusing the electric field in the flow direction to provide high field strength and gradient. The location of the trapped and concentrated particles depends on the strength of the electric field applied. Both 'streaming DEP' and 'trapping DEP' simultaneously take place within the concentrator at different regions. The former occurs upstream and is responsible for continuous transport of the particles, whereas the latter occurs downstream and rapidly traps the particles delivered from upstream. The performance of the device is demonstrated by successfully concentrating fluorescent nanoparticles. The described microfluidic concentrator can be implemented in applications where rapid concentration of targets is needed such as concentrating cells for sample preparation and concentrating molecular biomarkers for detection.
Keywords: DC dielectrophoresis; Electrokinetics; Microfluidics; Nanoparticles.
Figures


References
-
- Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD, editor. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and water Environment Federation, USA; 2005.
-
- Chen DF, Du H, Li WH. A 3D paired microelectrode array for accumulation and separation of microparticles. J. 2006;16:1162–1169. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/16/7/008. COI number [1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XptVKhur4%3D]; Bibcode number [2006JMiMi..16.1162C] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

