Kinetics and efficacy of an organophosphorus hydrolase in a rodent model of methyl-parathion poisoning
- PMID: 20653588
- PMCID: PMC2911639
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2010.00798.x
Kinetics and efficacy of an organophosphorus hydrolase in a rodent model of methyl-parathion poisoning
Abstract
Objectives: Organophosphorus (OP) pesticides exert a tremendous health burden, particularly in the developing world. Limited resources, the severity of intentional OP ingestions, and a paucity of beneficial therapies all contribute to the morbidity and mortality of this broad class of chemicals. A novel theoretical treatment for OP poisoning is the use of an enzyme to degrade the parent OP in the circulation after poisoning. The aims of this study were to determine the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of an OP hydrolase (OpdA) in a rodent model of severe methyl-parathion poisoning.
Methods: Two animal models were used. First, Wistar rats were administered two different doses of the hydrolase (0.15 and 1.5 mg/kg), and the ex vivo hydrolytic activity of plasma was determined by a fluorometric method. Second, an oral methyl-parathion animal poisoning model was developed to mimic severe human poisoning, and the efficacy of postpoisoning OpdA (as measured by survival to 4 and 24 hours) was determined.
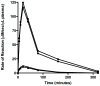
Results: The half-life of OpdA in the Wistar rat was dependent on the dose administered and ranged between 45.0 and 57.9 minutes. The poisoning model of three times the lethal dose to 50% of the population (3 x LD(50)) of methyl-parathion resulted in 88% lethality at 4 and 24 hours. Using a single dose of 0.15 mg/kg OpdA 10 minutes after poisoning resulted in 100% survival at 4 hours (p = 0.001 vs. placebo), but 0% at 24 hours postpoisoning (p = NS vs. placebo).
Conclusions: The OP hydrolase OpdA exhibits pharmacokinetics suitable for repeated dosing and increases short-term survival after severe methyl-parathion poisoning.
2010 by the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of an organophosphorus hydrolase enzyme (OpdA) in human serum and minipig models of organophosphorus insecticide poisoning.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020 May;58(5):397-405. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2019.1655149. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020. PMID: 31452424 Free PMC article.
-
OpdA, a bacterial organophosphorus hydrolase, prevents lethality in rats after poisoning with highly toxic organophosphorus pesticides.Toxicology. 2008 May 21;247(2-3):88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.02.005. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18378376 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of OpdA, an organophosphorus hydrolase, in the African green monkey.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Oct 1;80(7):1075-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.008. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599794 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl parathion: a review of health effects.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003 Mar-Apr;6(2):185-210. doi: 10.1080/10937400306471. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003. PMID: 12554434 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methyl parathion.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 2002 May;65(5):187-99. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 2002. PMID: 12166762 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro evaluation of the catalytic activity of paraoxonases and phosphotriesterases predicts the enzyme circulatory levels required for in vivo protection against organophosphate intoxications.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Nov 25;259(Pt B):252-256. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.04.039. Epub 2016 May 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27163850 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the calcium plateau in neuronal injury and behavioral morbidities following organophosphate intoxication.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Jun;1374(1):176-83. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13122. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016. PMID: 27327161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of new enzyme function: lessons from xenobiotic metabolizing bacteria versus insecticide-resistant insects.Evol Appl. 2011 Mar;4(2):225-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-4571.2010.00175.x. Evol Appl. 2011. PMID: 25567970 Free PMC article.
-
Use of OpdA, an organophosphorus (OP) hydrolase, prevents lethality in an African green monkey model of acute OP poisoning.Toxicology. 2014 Mar 20;317:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 24447378 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of an organophosphorus hydrolase enzyme (OpdA) in human serum and minipig models of organophosphorus insecticide poisoning.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020 May;58(5):397-405. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2019.1655149. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020. PMID: 31452424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeyaratnam J. Acute pesticide poisoning: a major global health problem. World Health Stat Q. 1990;43:139–44. - PubMed
-
- Sidell FR. Clinical effects of organophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitors. J Appl Toxicol. 1994;14:111–3. - PubMed
-
- Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P, Zilker T, Worek F. Correlation between red blood cell acetylcholinesterase activity and neuromuscular transmission in organophosphate poisoning. Chem Biol Interact. 2005;157–158:345–7. - PubMed
-
- Bird SB, Gaspari RJ, Dickson EW. Early death due to severe organophosphate poisoning is a centrally mediated process. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10:295–8. - PubMed
-
- Eddleston M, Singh S, Buckley N. Organophosphorus poisoning (acute) Clin Evid (BMJ) 2005;13:1744–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

