Global transcriptome profiling of wild soybean (Glycine soja) roots under NaHCO3 treatment
- PMID: 20653984
- PMCID: PMC3017823
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-153
Global transcriptome profiling of wild soybean (Glycine soja) roots under NaHCO3 treatment
Abstract
Background: Plant roots are the primary site of perception and injury for saline-alkaline stress. The current knowledge of saline-alkaline stress transcriptome is mostly focused on saline (NaCl) stress and only limited information on alkaline (NaHCO3) stress is available.
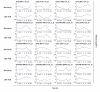
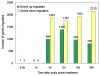
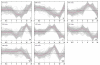
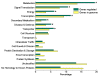
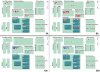
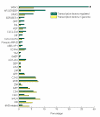
Results: Using Affymetrix Soybean GeneChip, we conducted transcriptional profiling on Glycine soja roots subjected to 50 mmol/L NaHCO3 treatment. In a total of 7088 probe sets, 3307 were up-regulated and 5720 were down-regulated at various time points. The number of significantly stress regulated genes increased dramatically after 3 h stress treatment and peaked at 6 h. GO enrichment test revealed that most of the differentially expressed genes were involved in signal transduction, energy, transcription, secondary metabolism, transporter, disease and defence response. We also detected 11 microRNAs regulated by NaHCO3 stress.
Conclusions: This is the first comprehensive wild soybean root transcriptome analysis under alkaline stress. These analyses have identified an inventory of genes with altered expression regulated by alkaline stress. The data extend the current understanding of wild soybean alkali stress response by providing a set of robustly selected, differentially expressed genes for further investigation.
Figures
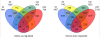


References
-
- Ge Y, Zhu YM, Lv DK, Dong TT, Wang WS, Tan SJ, Liu CH, Zou P. Research on responses of wild soybean to alkaline stress. Pratacultural Science. 2009;26(2):47–52.
-
- Kilian J, Whitehead D, Horak J, Wanke D, Weinl S, Batistic O, D'Angelo C, Bornberg-Bauer E, Kudla J, Harter K. The AtGenExpress global stress expression data set: protocols, evaluation and model data analysis of UV-B light, drought and cold stress responses. Plant Journal. 2007;50(2):347–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03052.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T. Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant Journal. 2002;31(3):279–292. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01359.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takahashi S, Seki M, Ishida J, Satou M, Sakurai T, Narusaka M, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Akiyama K. Monitoring the expression profiles of genes induced by hyperosmotic, high salinity, and oxidative stress and abscisic acid treatment in Arabidopsis cell culture using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant Molecular Biology. 2004;56:29–55. doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-2200-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

