Accumulation of neoplastic traits prior to spontaneous in vitro transformation of rat cholangiocytes determines susceptibility to activated ErbB-2/Neu
- PMID: 20655306
- PMCID: PMC4012332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.07.005
Accumulation of neoplastic traits prior to spontaneous in vitro transformation of rat cholangiocytes determines susceptibility to activated ErbB-2/Neu
Abstract
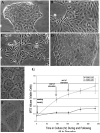
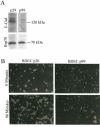
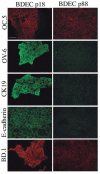
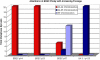
Cholangiocarcinoma, a severe form of biliary cancer, has a high mortality rate resulting partially from the advanced stage of disease at earliest diagnosis. A better understanding of the progressive molecular and cellular changes occurring during spontaneous cholangiocarcinogenesis is needed to identify potential biomarkers for diagnosis/prognosis or targets for novel therapeutics. Here, we show that with continued passage (p) in vitro, rat bile duct epithelial cells (BDEC) accumulated neoplastic characteristics that by mid-passage (p31-85) included alterations in morphology, increased growth rate, growth factor independence, decreased cell adhesion, loss of cholangiocyte markers expressed at low passage (p<30), and onset of aneuploidy. At high passage (p>85), BDEC cultures showed increasing numbers of cells expressing activated, tyrosine phosphorylated ErbB-2/Neu, a receptor tyrosine kinase previously reported to be at elevated levels in cholangiocarcinomas. Enrichment for high passage ErbB-2/Neu-positive cells yielded several anchorage-independent sub-lines with elevated levels of activated ErbB-2/Neu and increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). When injected into immunodeficient beige/nude/xid mice, these sub-lines formed poorly differentiated cystic tumors strongly positive for rat cholangiocyte markers, a finding consistent with a previous report showing the susceptibility of high passage, non-tumorigenic BDEC to transformation by activated ErbB-2/Neu. Mid passage BDEC, in contrast, were resistant to the transforming activity of activated ErbB-2/Neu and remained anchorage dependent in vitro and non-tumorigenic in vivo following stable transfection. Based on these findings, we concluded that during progression to high passage, cultured BDEC undergo preneoplastic changes that enhance their susceptibility to transformation by ErbB-2/Neu. The ability to generate cells at different points in the process of spontaneous neoplastic transformation offers a valuable model system for identifying molecular features that determine whether over-expression of activated ErbB-2/Neu is necessary and sufficient to induce neoplastic conversion.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
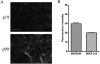

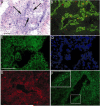

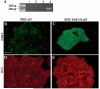
Similar articles
-
Differential gene expression profiling of cultured neu-transformed versus spontaneously-transformed rat cholangiocytes and of corresponding cholangiocarcinomas.Exp Mol Pathol. 2010 Dec;89(3):227-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.08.007. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20816680 Free PMC article.
-
erbB-2/neu transformed rat cholangiocytes recapitulate key cellular and molecular features of human bile duct cancer.Gastroenterology. 2005 Dec;129(6):2047-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.10.010. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 16344070
-
A novel "patient-like" model of cholangiocarcinoma progression based on bile duct inoculation of tumorigenic rat cholangiocyte cell lines.Hepatology. 2008 Apr;47(4):1178-90. doi: 10.1002/hep.22088. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18081149
-
Mechanisms of biliary carcinogenesis and growth.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 May 21;14(19):2986-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2986. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18494047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biliary cancer growth factor pathways, cyclo-oxygenase-2 and potential therapeutic strategies.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001 Apr;16(4):363-72. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2001.02438.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001. PMID: 11357901 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential gene expression profiling of cultured neu-transformed versus spontaneously-transformed rat cholangiocytes and of corresponding cholangiocarcinomas.Exp Mol Pathol. 2010 Dec;89(3):227-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.08.007. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20816680 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of preneoplastic and neoplastic rat mesothelial cell lines: the involvement of TETs, DNMTs, and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34664-87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8970. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27129173 Free PMC article.
-
Liver carcinogenesis: rodent models of hepatocarcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma.Dig Liver Dis. 2013 Jun;45(6):450-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2012.10.008. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Dig Liver Dis. 2013. PMID: 23177172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soft agar-based selection of spontaneously transformed rat prostate epithelial cells with highly tumorigenic characteristics.Exp Mol Pathol. 2018 Aug;105(1):89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 May 29. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29856983 Free PMC article.
-
The cholangiocyte marker, BD. 1, forms a stable complex with CLIP170 and shares an identity with eIF3a, a multifunctional subunit of the eIF3 initiation complex.Exp Mol Pathol. 2012 Oct;93(2):250-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.04.023. Epub 2012 May 18. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22613460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavallaro U, Christofori G. Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:118–32. - PubMed
-
- Cheung P, Tanner KG, Cheung WL, Sassone-Corsi P, Denu JM, Allis CD. Synergistic coupling of histone H3 phosphorylation and acetylation in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation. Mol Cell. 2000;5:905–15. - PubMed
-
- Darcy KM, Zangani D, Wohlhueter AL, Huang RY, Vaughan MM, Russell JA, Ip MM. Changes in ErbB2 (her-2/neu), ErbB3, and ErbB4 during growth, differentiation, and apoptosis of normal rat mammary epithelial cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 2000;48:63–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

