Crossover invariance determined by partner choice for meiotic DNA break repair
- PMID: 20655467
- PMCID: PMC2911445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.05.041
Crossover invariance determined by partner choice for meiotic DNA break repair
Abstract
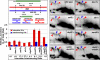
Crossovers between meiotic homologs are crucial for their proper segregation, and crossover number and position are carefully controlled. Crossover homeostasis in budding yeast maintains crossovers at the expense of noncrossovers when double-strand DNA break (DSB) frequency is reduced. The mechanism of maintaining constant crossover levels in other species has been unknown. Here we investigate in fission yeast a different aspect of crossover control--the near invariance of crossover frequency per kb of DNA despite large variations in DSB intensity across the genome. Crossover invariance involves the choice of sister chromatid versus homolog for DSB repair. At strong DSB hotspots, intersister repair outnumbers interhomolog repair approximately 3:1, but our genetic and physical data indicate the converse in DSB-cold regions. This unanticipated mechanism of crossover control may operate in many species and explain, for example, the large excess of DSBs over crossovers and the repair of DSBs on unpaired chromosomes in diverse species.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

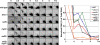



Similar articles
-
Mus81-Eme1-dependent and -independent crossovers form in mitotic cells during double-strand break repair in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 May;27(10):3828-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01596-06. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17353272 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionarily diverse determinants of meiotic DNA break and recombination landscapes across the genome.Genome Res. 2014 Oct;24(10):1650-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.172122.114. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 25024163 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1003978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003978. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367271 Free PMC article.
-
New and old ways to control meiotic recombination.Trends Genet. 2011 Oct;27(10):411-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Trends Genet. 2011. PMID: 21782271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Making crossovers during meiosis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1451-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0331451. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246144 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered distribution of MLH1 foci is associated with changes in cohesins and chromosome axis compaction in an asynaptic mutant of tomato.Chromosoma. 2012 Jun;121(3):291-305. doi: 10.1007/s00412-012-0363-z. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Chromosoma. 2012. PMID: 22350750
-
Gradual implementation of the meiotic recombination program via checkpoint pathways controlled by global DSB levels.Mol Cell. 2015 Mar 5;57(5):797-811. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.027. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25661491 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving complex chromosome structures during meiosis: versatile deployment of Smc5/6.Chromosoma. 2016 Mar;125(1):15-27. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0518-9. Epub 2015 May 7. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 25947290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel attributes of Hed1 affect dynamics and activity of the Rad51 presynaptic filament during meiotic recombination.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 6;287(2):1566-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.297309. Epub 2011 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22115747 Free PMC article.
-
DNA sequence differences are determinants of meiotic recombination outcome.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 11;9(1):16446. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52907-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31712578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allers T, Lichten M. Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell. 2001;106:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Ashley T, Plug AW, Xu J, Solari AJ, Reddy G, Golub EI, Ward DC. Dynamic changes in Rad51 distribution on chromatin during meiosis in male and female vertebrates. Chromosoma. 1995;104:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Baudat F, de Massy B. Regulating double-stranded DNA break repair towards crossover or non-crossover during mammalian meiosis. Chromosome Res. 2007;15:565–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

