B-lymphocyte homeostasis and BLyS-directed immunotherapy in transplantation
- PMID: 20655723
- PMCID: PMC2946495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trre.2010.05.004
B-lymphocyte homeostasis and BLyS-directed immunotherapy in transplantation
Abstract
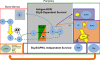
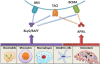
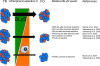
Current strategies for immunotherapy after transplantation are primarily T-lymphocyte directed and effectively abrogate acute rejection. However, the reality of chronic allograft rejection attests to the fact that transplantation tolerance remains an elusive goal. Donor-specific antibodies are considered the primary cause of chronic rejection. When naive, alloreactive B-cells encounter alloantigen and are activated, a resilient "sensitized" state, characterized by the presence of high-affinity antibody, is established. Here, we will delineate findings that support transient B-lymphocyte depletion therapy at the time of transplantation to preempt sensitization by eliminating alloreactive specificities from the recipient B-cell pool (ie, "repertoire remodeling"). Recent advances in our understanding of B-lymphocyte homeostasis provide novel targets for immunomodulation in transplantation. Specifically, the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine BLyS is the dominant survival factor for "tolerance-susceptible" transitional and "preimmune" mature follicular B-cells. The transitional phenotype is the intermediate through which all newly formed B-cells pass before maturing into the follicular subset, which is responsible for mounting an alloantigen-specific antibody response. Systemic BLyS levels dictate the stringency of negative selection during peripheral B-cell repertoire development. Thus, targeting BLyS will likely provide an opportunity for repertoire-directed therapy to eliminate alloreactive B-cell specificities in transplant recipients, a requirement for the achievement of humoral tolerance and prevention of chronic rejection. In this review, the fundamentals of preimmune B-cell selection, homeostasis, and activation will be described. Furthermore, new and current B-lymphocyte-directed therapy for antibody-mediated rejection and the highly sensitized state will be discussed. Overall, our objective is to propose a rational approach for induction of humoral transplantation tolerance by remodeling the primary B-cell repertoire of the allograft recipient.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Terasaki PI, Cai J. Human leukocyte antigen antibodies and chronic rejection: from association to causation. Transplantation. 2008;86(3):377. - PubMed
-
- Colvin RB. Pathology of chronic humoral rejection. Contrib Nephrol. 2009;162:75. - PubMed
-
- Colvin RB, Smith RN. Antibody-mediated organ-allograft rejection. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(10):807. - PubMed
-
- Jordan SC, Pescovitz MD. Presensitization: the problem and its management. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1(3):421. - PubMed
-
- Kirk AD, Baldwin WM, Cascalho MI, Chong AS, Sykes M, West LJ. American society of transplantation symposium on B cells in transplantation: harnessing humoral immunity from rodent models to clinical practice. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:1464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

