Chronic amphetamine treatment enhances corticotropin-releasing factor-induced serotonin release in the amygdala
- PMID: 20655906
- PMCID: PMC2923226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.07.008
Chronic amphetamine treatment enhances corticotropin-releasing factor-induced serotonin release in the amygdala
Abstract
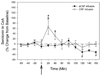
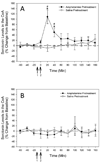
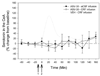
Amphetamine use is associated with dysphoric states, including heightened anxiety, that emerge within 24h of withdrawal from the drug. Corticotropin-releasing factor increases serotonin release in the central nucleus of the amygdala, and this neurochemical circuitry may play a role in mediating fear and anxiety states. We have previously shown that chronic amphetamine treatment increases corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type-2 levels in the serotonergic dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat. Therefore, we hypothesized that chronic amphetamine treatment would enhance the amygdalar serotonergic response to corticotropin-releasing factor infused into the dorsal raphe nucleus. Male rats were injected once-daily with d-amphetamine (2.5mg/kg i.p., or saline) for two weeks. Serotonin release within the central nucleus of the amygdala in response to intra-raphe infusion of corticotropin-releasing factor (100 ng) was measured 24h after the last treatment in urethane-anesthetized (1.8 mg/kg, i.p.) rats using in vivo microdialysis. Rats pretreated with amphetamine showed significantly enhanced serotonin release in the central nucleus of the amygdala in response to corticotropin-releasing factor infusion when compared to saline pretreated rats. Furthermore, this enhanced response was blocked by the corticotropin-releasing factor type-2 receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30 (2 microg) infused into the dorsal raphe nucleus. These results suggest increased sensitivity to corticotropin-releasing factor as mediated by type-2 receptors following chronic amphetamine treatment, which may underlie dysphoric states observed during amphetamine withdrawal.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Amat J, Tamblyn JP, Paul ED, Bland ST, Amat P, Foster AC, Watkins LR, Maier SF. Microinjection of urocortin 2 into the dorsal raphe nucleus activates serotonergic neurons and increases extracellular serotonin in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience. 2004;129:509–519. - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam JD, Hornig-Rohan M, Maislin G. Efficacy of alprazolam in reducing fluoxetine-induced jitteriness in patients with major depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994;55:394–400. - PubMed
-
- Artaiz I, Zazpe A, Del Rio J. Characterization of serotonergic mechanisms involved in the behavioural inhibition induced by 5-hydroxytryptophan in a modified light-dark test in mice. Behavioural Pharmacol. 1998;9:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL. Sensitivity to stress: dysregulation of CRF pathways and disease development. Horm. Behav. 2005;48:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Barr AM, Markou A. Psychostimulant withdrawal as an inducing condition in animal models of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005;29:675–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

