Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)-mediated expression and function of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) in granulosa cells
- PMID: 20655982
- PMCID: PMC5010784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.07.018
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)-mediated expression and function of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) in granulosa cells
Abstract
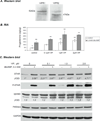
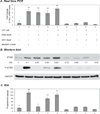
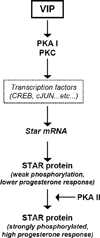
VIP is a peptide hormone capable of activating the cAMP/PKA pathway and modifying gonadal steroidogenic capacity. Less is known about the molecular mechanisms of VIP-mediated steroidogenesis and its role in regulating the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (STAR). We examined the impact of VIP on STAR expression and function in immortalized (KK1) and primary mouse granulosa cells, where VIP strongly upregulated STAR expression and steroidogenesis. Inhibitors of the PKA and PKC pathways suggested that both are activated by VIP. VIP did not efficiently phosphorylate STAR (P-STAR); however, VIP together with cAMP-analogs that activate Type II PKA increased P-STAR and further increased steroidogenesis. Our results suggest that VIP-induced STAR expression and function in granulosa cells result from the preferential activation of Type I PKA. Furthermore, the PKA and PKC pathways appear to converge at regulating VIP-mediated Star transcription and translation.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of action of hormone-sensitive lipase in mouse Leydig cells: its role in the regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8505-8518. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417873. Epub 2013 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23362264 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-independent signaling regulates steroidogenesis in mouse Leydig cells in the absence of StAR phosphorylation.J Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Aug;37(1):81-95. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.02065. J Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16901926
-
Interplay of PI3K and cAMP/PKA signaling, and rapamycin-hypersensitivity in TGFbeta1 enhancement of FSH-stimulated steroidogenesis in rat ovarian granulosa cells.J Endocrinol. 2007 Feb;192(2):405-19. doi: 10.1677/JOE-06-0076. J Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17283241
-
Regulation of expression of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene: a central role for steroidogenic factor 1.Steroids. 1997 Jan;62(1):5-9. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(96)00152-3. Steroids. 1997. PMID: 9029708 Review.
-
Knowledge Gap in Understanding the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Regulation in Steroidogenesis Following Exposure to Bisphenol A and Its Analogues.Biomedicines. 2022 May 30;10(6):1281. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061281. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) in polycystic ovary syndrome patients undergoing IVF.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 7;15:1331282. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1331282. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38774232 Free PMC article.
-
The Neural Signals of the Superior Ovarian Nerve Modulate in an Asymmetric Way the Ovarian Steroidogenic Response to the Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide.Front Physiol. 2018 Aug 20;9:1142. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01142. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30177887 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Induced Inflammation in an Immortalized Ovine Luteal Endothelial Cell Line (OLENDO).Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 24;9(3):99. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9030099. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35324827 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted reproduction, estrous cycle, and circadian rhythms in female mice deficient in vasoactive intestinal peptide.J Biol Rhythms. 2014 Oct;29(5):355-69. doi: 10.1177/0748730414549767. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Biol Rhythms. 2014. PMID: 25252712 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric steroidogenic response by the ovaries to the vasoactive intestinal peptide.Endocrine. 2015 Apr;48(3):968-77. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0449-x. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Endocrine. 2015. PMID: 25331816
References
-
- Abe H, Engler D, Molitch ME, Bollinger-Gruber J, Reichlin S. Vasoactive intestinal peptide is a physiological mediator of prolactin release in the rat. Endocrinology. 1985;116:1383–1390. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed CE, Dees WL, Ojeda SR. The immature rat ovary is innervated by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)-containing fibers and responds to VIP with steroid secretion. Endocrinology. 1986;118:1682–1689. - PubMed
-
- Alm P, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Owman O, Sjöberg NO, Sundler F, Walles B. Origin and distribution of VIP (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide)-nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;205:337–347. - PubMed
-
- Bajo AM, Juarranz MG, Valenzuela P, Martínez P, Prieto JC, Guijarro LG. Expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptors in human uterus. Peptides. 2000;21:1383–1388. - PubMed
-
- Barberi M, Muciaccia B, Morelli MB, Stefanini M, Cecconi S, Canipari R. Expression localisation and functional activity of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and their receptors in mouse ovary. Reproduction. 2007;134:281–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

