fMRI evidence of neural abnormalities in the subcortical face processing system in ASD
- PMID: 20656041
- PMCID: PMC3426450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.037
fMRI evidence of neural abnormalities in the subcortical face processing system in ASD
Abstract
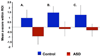
Recent evidence suggests that a rapid, automatic face detection system is supported by subcortical structures including the amygdala, pulvinar, and superior colliculus. Early-emerging abnormalities in these structures may be related to reduced social orienting in children with autism, and subsequently, to aberrant development of cortical circuits involved in face processing. Our objective was to determine whether functional abnormalities in the subcortical face processing system are present in adults with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) during supraliminal fearful face processing. Participants included twenty-eight individuals with ASD and 25 controls group-matched on age, IQ, and behavioral performance. The ASD group met diagnostic criteria on the ADI-R, ADOS-G, and DSM-IV. Both the ASD and control groups showed significant activation in bilateral fusiform gyri. The control group exhibited additional significant responses in the right amygdala, right pulvinar, and bilateral superior colliculi. In the direct group comparison, the controls showed significantly greater activation in the left amygdala, bilateral fusiform gyrus, right pulvinar, and bilateral superior colliculi. No brain region showed significantly greater activation in the ASD group compared to the controls. Thus, basic rapid face identification mechanisms appear to be functional in ASD. However, individuals with ASD failed to engage the subcortical brain regions involved in face detection and automatic emotional face processing, suggesting a core mechanism for impaired socioemotional processing in ASD. Neural abnormalities in this system may contribute to early-emerging deficits in social orienting and attention, the putative precursors to abnormalities in social cognition and cortical face processing specialization.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neural circuitry of emotional face processing in autism spectrum disorders.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010 Mar;35(2):105-14. doi: 10.1503/jpn.090085. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20184808 Free PMC article.
-
Association between amygdala response to emotional faces and social anxiety in autism spectrum disorders.Neuropsychologia. 2010 Oct;48(12):3665-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.07.022. Epub 2010 Jul 22. Neuropsychologia. 2010. PMID: 20655320 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorders during face processing.Brain. 2008 Apr;131(Pt 4):1000-12. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm334. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Brain. 2008. PMID: 18234695
-
Research review: Constraining heterogeneity: the social brain and its development in autism spectrum disorder.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2011 Jun;52(6):631-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02349.x. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21244421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Neural mechanisms of facial recognition].Brain Nerve. 2007 Jan;59(1):45-51. Brain Nerve. 2007. PMID: 17354378 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Cortical networks for face perception in two-month-old infants.Proc Biol Sci. 2014 Oct 22;281(1793):20141468. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.1468. Proc Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25185999 Free PMC article.
-
Neural signatures of autism spectrum disorders: insights into brain network dynamics.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jan;40(1):171-89. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.172. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25011468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Dynamics of the fMRI Response to Faces in Individuals with Autism.J Autism Dev Disord. 2016 Jan;46(1):232-241. doi: 10.1007/s10803-015-2565-8. J Autism Dev Disord. 2016. PMID: 26340957 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the amygdala in atypical gaze on emotional faces in autism spectrum disorders.J Neurosci. 2012 Jul 11;32(28):9469-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5294-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22787032 Free PMC article.
-
Neural networks related to dysfunctional face processing in autism spectrum disorder.Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Jul;220(4):2355-71. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0791-z. Epub 2014 May 29. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 24869925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolphs R, Sears L, Piven J. Abnormal processing of social information from faces in autism. J Cogn Neurosci. 2001;13:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D. Amygdala damage impairs emotion recognition from scenes only when they contain facial expressions. Neuropsychologia. 2003;41:1281–1289. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Ashwin C, Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, O'Riordan M, Bullmore ET. Differential activation of the amygdala and the 'social brain' during fearful face-processing in Asperger Syndrome. Neuropsychologia. 2006a - PubMed
-
- Ashwin C, Chapman E, Colle L, Baron-Cohen S. Impaired recognition of negative basic emotions in autism: a test of the amygdala theory. Soc Neurosci. 2006b;1:349–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

